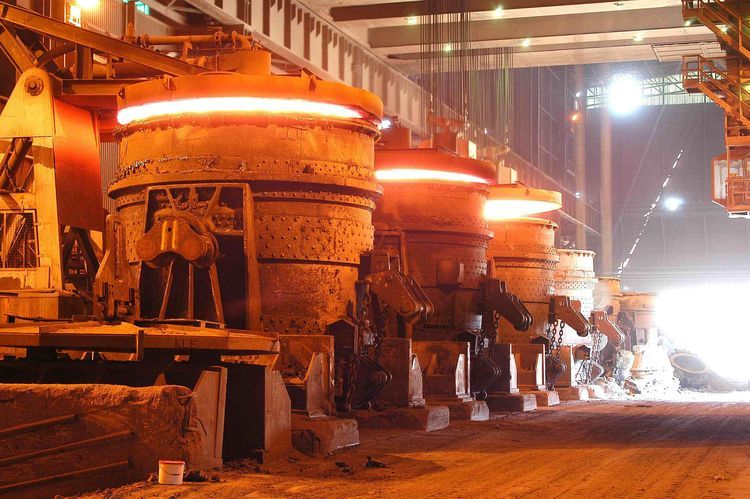
In modern steelmaking, every component inside the ladle plays a crucial role in ensuring clean steel, stable flow control, and safe casting operations. Among these components, the ladle slide gate plate is one of the most important refractory elements. It directly influences the efficiency of molten steel flow control, the performance of the ladle, and the overall stability of continuous casting. Although it is a small part relative to the scale of a steel plant, its function is vital and highly technical.
This article explains what a ladle slide gate plate is, its key uses, how it works, types, material characteristics, benefits, and factors that influence its service life. Whether you are a procurement manager, refractory engineer, or metallurgical professional, this in-depth overview will help you better understand the importance of choosing the right ladle slide gate plate.
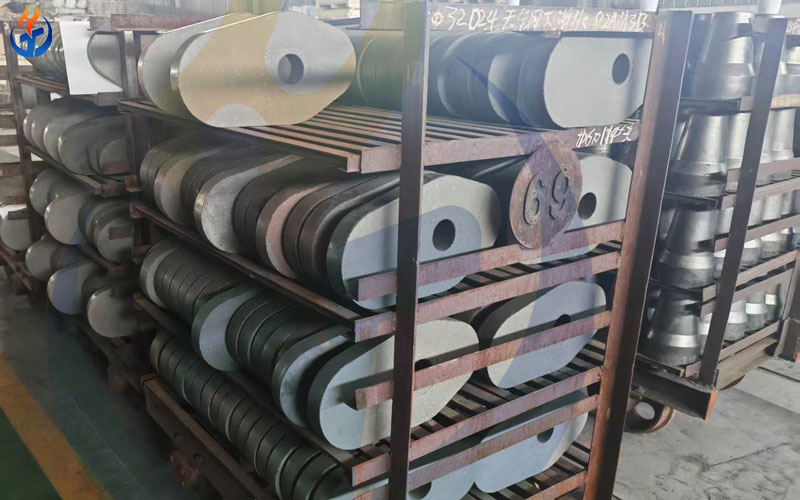

What Is a Ladle Slide Gate Plate?
A ladle slide gate plate is a refractory component installed at the bottom of a steel ladle. It works together with the nozzle, collector nozzle, and upper plate to control the opening and closing of molten steel flow during casting.
The slide gate plate moves in a horizontal sliding motion, adjusting the orifice alignment to open, regulate, or shut off molten steel flow. Due to extreme temperatures (up to 1600°C), strong thermal shocks, and high mechanical stress, slide gate plates are typically made from high-performance refractory materials such as:
Alumina-carbon
Zirconia-carbon
High-purity alumina
Refractory composites reinforced with pitch or resin
The design and material of the ladle slide gate plate determine its performance during casting operations, especially in demanding long-sequence continuous casting conditions.
What Is the Use of Ladle Slide Gate Plate?
The main use of a ladle slide gate plate is to control molten steel flow from the ladle during steelmaking. More specifically, the ladle slide gate plate is used for:
2.1 Opening and Stopping Molten Steel Flow
This is the most critical function. When the slide gate plate moves, it aligns (or misaligns) the opening between the upper and lower nozzles, controlling:
Start of casting
Shut-off during ladle change
Emergency stopping in case of abnormal flow
Without a reliable ladle slide gate plate, operators cannot safely transfer molten steel to tundish or molds.
2.2 Adjusting Flow Rate During Continuous Casting
Different steel grades and casting speeds require precise flow control.
The ladle slide gate plate allows:
Fine adjustment of orifice opening
Stable flow during long casting sequences
Prevention of overflow or turbulence
This flow regulation helps ensure uniform casting and high-quality steel.
2.3 Preventing Molten Steel Leakage
A tight seal between the slide gate plate and nozzles is essential.
A high-quality ladle slide gate plate:
Prevents leakage
Reduces the risk of breakout
Maintains casting safety
Leakage incidents can lead to costly downtime and equipment damage.
2.4 Improving Steel Purity
A properly functioning ladle slide gate plate reduces:
Reoxidation
Slag entrapment
Inclusion formation
Stable flow means fewer chances for impurities entering the tundish, leading to cleaner steel.
2.5 Extending Ladle Campaign Life
Even wear leads to:
Fewer ladle repairs
Reduced refractory consumption
Longer ladle service cycles
Because ladle slide gate plates withstand both chemical and mechanical attack, selecting high-quality plates supports long-term cost savings.
How a Ladle Slide Gate Plate Works
The slide gate system typically consists of:
Upper slide plate
Lower slide plate
Nozzle set (upper nozzle + collector nozzle)
Sliding mechanism and housing
During operation:
Molten steel stays inside the ladle, supported by closed aligned plates.
When the operator pulls the lever or hydraulic system activates, the ladle slide gate plate moves laterally.
This movement aligns the openings, allowing molten steel to pass through the nozzle.
Flow rate changes according to plate movement (partial or full opening).
When casting is complete, the plate returns to the closed position, stopping steel flow.
The smooth operation depends largely on:
Plate surface finish
Material hardness
Wear resistance
Proper matching between upper and lower plates
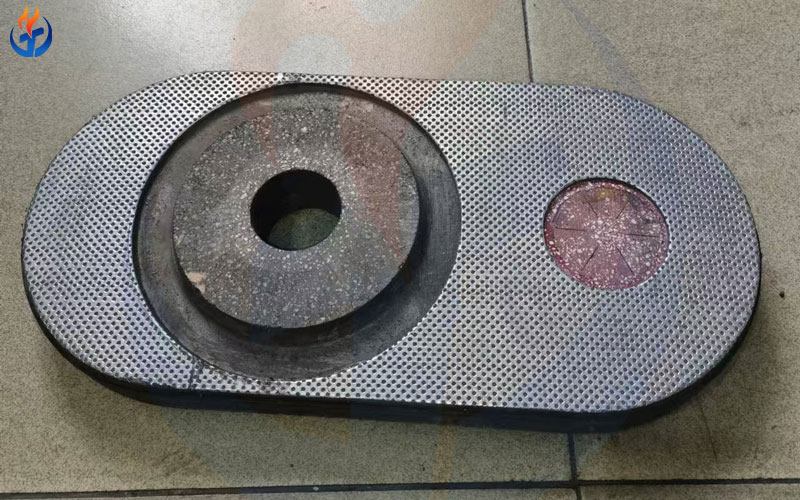

Types of Ladle Slide Gate Plates
Different steel plants use different slide gate technologies. Common types include:
4.1 Single-Plate Slide Gate System
Traditional design
Simple structure
Mostly used in small ladles or low-intensity casting
4.2 Multi-Plate (Two-Plate or Three-Plate) Systems
Allows finer flow control
Better sealing performance
Suitable for medium-to-large steel ladles
4.3 Hydraulic Slide Gate Plate Systems
Precise movement
Automated control
Ideal for continuous casting with strict speed requirements
4.4 High-Performance ZrO₂-Enriched Plate
Excellent thermal shock resistance
Very high erosion and corrosion resistance
Used for long sequence casting or alloy steel production
Understanding which type suits your ladle and steel grade is key for optimal performance.
Material Properties of a High-Quality Ladle Slide Gate Plate
To withstand rapid heating, cooling, corrosion, and mechanical stress, plates must meet strict quality standards.
5.1 Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance
Rapid temperature changes occur when molten steel first contacts the plate. Materials like alumina-carbon and zirconia-carbon maintain structural integrity under thermal cycling.
5.2 High Density and Low Porosity
Low porosity:
Improves mechanical strength
Reduces slag penetration
Increases service life
5.3 Superior Wear Resistance
Plates slide against each other under pressure, requiring:
Smooth surface finish
Anti-friction additives
Strong bonding matrix
5.4 Strong Corrosion Resistance
Molten steel and slag aggressively attack refractories. Carbon bonding and ZrO₂ additions help prevent erosion and chemical wear.
5.5 Stable High-Temperature Strength
Plates must retain strength even at temperatures exceeding 1500°C. High-purity alumina composites perform exceptionally well.
Key Benefits of Using High-Quality Ladle Slide Gate Plates
The use of a durable and reliable ladle slide gate plate provides benefits such as:
6.1 Improved Casting Safety
No steelmaker wants a breakout incident. High-quality plates minimize leakage risk and ensure safe, stable operation.
6.2 Consistent Metallurgical Quality
Better flow control reduces slag entrapment and reoxidation, resulting in cleaner and more uniform steel.
6.3 Reduced Downtime
Longer plate life means fewer system changes and smoother production schedules.
6.4 Cost-Effective Operation
Even though high-performance plates cost more upfront, they reduce:
Emergency repairs
Unexpected downtime
Refractory consumption
Casting interruptions
Over time, this saves significant operational costs.
6.5 Better Compatibility with Automation
Modern steel mills increasingly rely on automated casting. High-precision ladle slide gate plates are essential for seamless integration with hydraulic and sensor-controlled equipment.
Conclusion
The ladle slide gate plate is a crucial component in steelmaking, responsible for regulating molten steel flow, ensuring operational safety, and maintaining casting quality. Its use extends beyond simple flow control—it directly impacts productivity, steel purity, and equipment longevity.
By understanding what a ladle slide gate plate does and how it works, steel producers can choose the best materials and designs for their ladle systems. High-quality plates provide stable performance, longer service life, and significant long-term cost savings.
If you need help choosing high-performance ladle slide gate plates for your steelmaking operations, feel free to request customized technical recommendations.