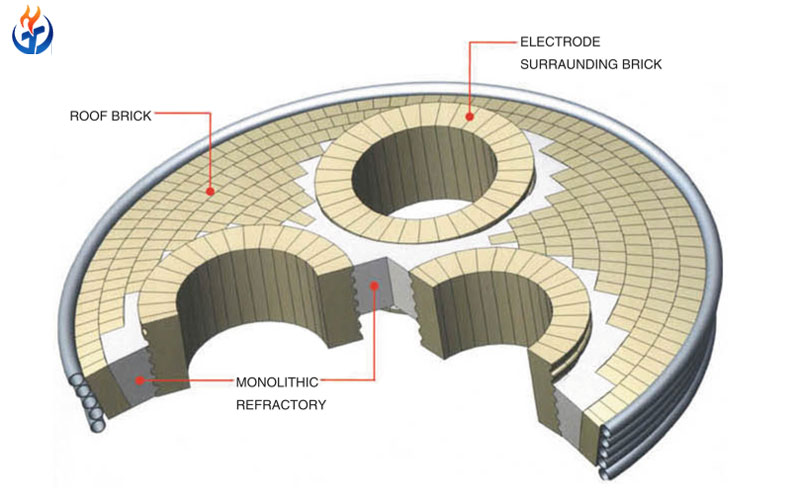
In glass manufacturing, Refractory Bricks for Glass Kilns play a critical role in ensuring efficient, safe, and long-lasting furnace operation. The extreme heat, chemical attack from molten glass, and constant temperature fluctuations put intense stress on kiln linings. Choosing the right refractory brick can mean the difference between consistent production and costly downtime.
In this guide, we’ll explore the top 9 types of refractory bricks used in glass kilns, highlighting their compositions, properties, and ideal applications. Whether you are operating a container glass plant, float glass furnace, or specialty glass production line, this list will help you make informed decisions.
1. Fused Cast AZS Bricks
Fused cast AZS (Alumina-Zirconia-Silica) bricks are among the most common refractory materials in the glass industry. They are produced by melting raw materials in an electric furnace and casting them into molds before annealing.
Key properties:
Exceptional resistance to molten glass corrosion
Low glass phase exudation
Excellent thermal shock resistance
Applications:
Ideal for furnace superstructures, sidewalls, and feeder channels in container glass and float glass furnaces.
2. Silica Bricks
Silica bricks are made from quartz stone and are well-known for their high refractoriness and ability to maintain structural strength at elevated temperatures.
Key properties:
Refractoriness above 1700°C
Excellent resistance to acidic slags
Stable volume under high heat
Applications:
Used in the crown and upper structures of glass melting furnaces, where high-temperature stability is essential.
3. Fireclay Bricks
Fireclay bricks are one of the oldest and most cost-effective options for kiln construction. They are made from refractory clays with an alumina content of around 30–45%.
Key properties:
Good mechanical strength
Moderate thermal shock resistance
Affordable and widely available
Applications:
Best suited for non-critical zones such as flues, regenerators, and working ends.
4. Magnesia Bricks
Magnesia bricks are composed mainly of periclase (MgO) and are known for their strong resistance to basic slags.
Key properties:
High refractoriness
Excellent corrosion resistance to alkaline materials
Good load-bearing capacity at high temperatures
Applications:
Used in regenerator checkers and areas exposed to basic vapors.
5. High Alumina Bricks
These bricks have an alumina content ranging from 50% to 90%, making them suitable for zones requiring high strength and resistance to molten glass attack.
Key properties:
High load softening temperature
Excellent wear resistance
Good chemical stability
Applications:
Common in feeder channels, forehearths, and burner blocks.
6. Fused Cast Alumina Bricks
Made from pure alumina raw materials, fused cast alumina bricks offer outstanding resistance to alkali vapors and thermal shock.
Key properties:
High purity and corrosion resistance
Low glass pollution risk
Excellent thermal stability
Applications:
Preferred for glass contact areas where product purity is critical, such as specialty glass or optical glass furnaces.
7. Zircon Bricks
Zircon bricks contain over 65% zircon (ZrSiO4), giving them high corrosion resistance and low thermal expansion.
Key properties:
Excellent molten glass resistance
Low thermal conductivity
Minimal thermal expansion
Applications:
Used in throat, sidewall, and paving blocks of glass furnaces.
8. Insulating Fire Bricks (IFB)
While insulating fire bricks cannot withstand direct molten glass contact, they are important for conserving heat and reducing fuel costs.
Key properties:
Lightweight with low thermal conductivity
Good insulation capacity
Easy to cut and shape
Applications:
Installed behind dense refractory linings as a backup layer to reduce heat loss.
9. Chrome Corundum Bricks
These bricks combine alumina with chromium oxide, providing excellent resistance to both acid and basic slags.
Key properties:
Strong wear resistance
High refractoriness under load
Good thermal shock stability
Applications:
Used in high-stress zones like burner blocks, throat areas, and sidewalls.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Refractory Bricks for Glass Kilns
Selecting the right Refractory Bricks for Glass Kilns involves more than just knowing the temperature range. Consider these factors:
Type of Glass Produced
Different glasses (soda-lime, borosilicate, lead crystal) have varying chemical interactions with refractory materials.Operating Temperature
Higher temperatures require bricks with better refractoriness and load-bearing capacity.Corrosion Resistance
Bricks in contact with molten glass need exceptional corrosion resistance to maintain service life.Thermal Shock Resistance
Frequent temperature fluctuations demand materials that can withstand rapid heating and cooling.Energy Efficiency
Incorporating insulating layers can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Choosing the right Refractory Bricks for Glass Kilns is essential for optimizing furnace performance, minimizing downtime, and producing high-quality glass. From fused cast AZS bricks for corrosion resistance to insulating fire bricks for energy efficiency, each type has its strengths and ideal applications. By understanding these options, glass manufacturers can extend furnace life and improve productivity.
Whether you are upgrading an existing furnace or building a new one, partnering with an experienced refractory supplier ensures you get the most suitable brick for each zone of your kiln.