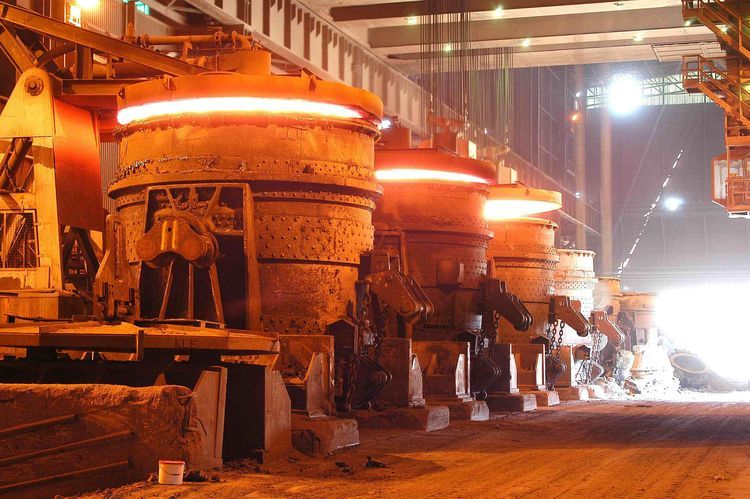
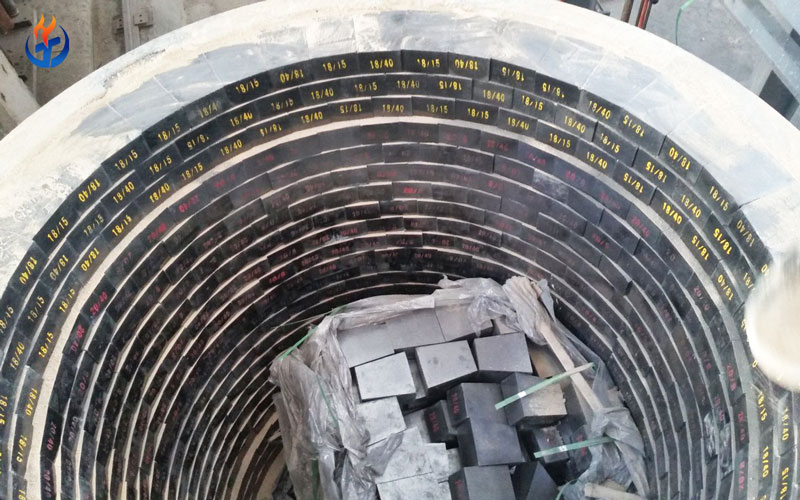
In the world of energy generation, thermal power plants remain one of the most widespread methods for producing electricity. These plants operate under intense heat and harsh conditions, particularly within their boilers, furnaces, and incinerators. To withstand such extreme environments, the selection and maintenance of refractory materials for thermal power plants become critically important.
Properly chosen thermal power refractory materials help reduce heat loss, improve efficiency, and prolong equipment life, ultimately contributing to lower operational costs and higher energy output. This article explores the types, applications, and best practices for using refractory materials and power plant bricks in thermal power plants.

Importance of Refractory Materials in Thermal Power Plants
The core operations in a thermal power plant—such as fuel combustion, steam generation, and flue gas processing—involve extremely high temperatures that can exceed 1400°C (2550°F). To protect structural components like boiler tubes, walls, ducts, ash hoppers, and furnaces from heat damage, refractory linings act as a crucial thermal barrier.
Key functions of thermal power refractory materials include:
Thermal insulation to minimize energy loss
Corrosion resistance against chemical attacks from fuel ash and gases
Mechanical strength to withstand abrasion and physical stress
Creep resistance under prolonged high temperatures
Structural stability during thermal cycling and rapid temperature changes
Without reliable power plant bricks and castables, the integrity of critical components can deteriorate rapidly, leading to unplanned shutdowns, costly repairs, or safety risks.
Common Areas of Refractory Use in Power Plants
Different zones of a thermal power plant require specific types of refractory materials, each tailored to the local temperature, atmosphere, and mechanical wear.
Boiler Furnaces
Boiler furnaces are the hottest zones in thermal power plants, often burning coal, oil, biomass, or refuse. Refractories here must resist slag corrosion, flame impingement, and high thermal shock.
Recommended materials:
High alumina bricks
Refractory castables with silicon carbide
Low cement castables for better strength and density
Burners and Combustion Chambers
These zones face direct flame impact and rapid thermal cycling. Refractories need to be highly insulating and shock-resistant.
Recommended materials:
Ceramic fiber modules
High-strength insulating fire bricks
Ash Hoppers and Dust Collectors
Ash from burned fuel accumulates in hoppers and passes through ducts where it causes abrasion and chemical corrosion.
Recommended materials:
Abrasion-resistant castables
Mullite-based bricks
Flue Gas Ducts and Chimneys
Flue gas areas operate at lower temperatures but with high moisture and corrosive gases like SO₂ and NOx.
Recommended materials:
Acid-resistant bricks
Insulating castables
Types of Thermal Power Refractory Materials
The choice of thermal power refractory materials depends on operating conditions. Here are some widely used categories:
(1) Refractory Bricks (Power Plant Bricks)
Bricks are commonly used due to their ease of installation, shape consistency, and wide range of formulations.
High alumina bricks: Used in combustion zones and high-temperature areas
Silica bricks: Excellent thermal shock resistance
Fireclay bricks: Cost-effective for moderate-temperature zones
Acid-resistant bricks: Suitable for flue gas zones
These power plant bricks offer long service life and structural reliability.
(2) Refractory Castables
Unshaped materials mixed and cast on-site, suitable for complex geometries or quick repairs.
Low cement castables (LCC): High density, low porosity
Medium cement castables: Good for general-purpose lining
Insulating castables: Ideal for heat retention and energy savings
(3) Ceramic Fiber Products
Fiber blankets, boards, and modules used for lining boiler walls and ducts where weight reduction is important.
Lightweight
Excellent insulation
Quick installation
(4) Plastic Refractories and Ramming Mixes
Used for patching, sealing, and lining tight or irregular areas like burner nozzles and boiler corners.
Criteria for Selecting Refractory Materials in Power Plants
When choosing thermal power refractory solutions, plant operators should consider several factors:
Operating Temperature Range
Each material has a maximum service temperature. Exceeding this limit can lead to rapid degradation.
Chemical Compatibility
Coal, biomass, or waste fuels can produce alkali or acidic ash, affecting refractory integrity. Alkali-resistant or acid-resistant materials are a must.
Abrasion and Erosion Resistance
Fly ash and slag are abrasive. Areas with high material flow need strong, dense refractories.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Castables are more adaptable to shape, while bricks are better for structure. Installation time, skill, and repair accessibility should be considered.
Thermal Conductivity
Lower thermal conductivity improves insulation, saving energy and protecting outer shell components.
Maintenance and Repair of Power Plant Refractories
Even with the best refractory lining, the kiln shell still faces risks, especially if the lining is compromised. Here are a few strategies to ensure effective shell protection:
Proper Lining Thickness
Ensure that lining thickness is sufficient to maintain an acceptable shell temperature (usually under 400°C/752°F). Too thin, and the shell overheats; too thick, and heat loss increases.
Regular Shell Temperature Monitoring
Using infrared sensors or laser scanning systems to continuously monitor the shell temperature allows early detection of hot spots.
Use of Backup Insulation
In some high-heat zones, insulation bricks or fiber blankets can be installed behind the main lining to prevent heat from reaching the shell.
Expansion Gaps
Allow for thermal expansion of bricks to prevent cracking or lining collapse.
Refractory Anchors
In monolithic lining applications, anchors help hold the material in place and reduce the risk of spalling.
Conclusion
Refractory materials are the unsung heroes of modern thermal power plants, silently withstanding extreme temperatures, corrosion, and wear every day. Whether it’s high-strength power plant bricks in a boiler wall or flexible castables in a burner throat, choosing the right thermal power refractory solution is vital to keeping operations safe, efficient, and cost-effective.
As energy production evolves, so too must refractory solutions—meeting the demands of cleaner fuels, higher efficiency targets, and longer service intervals. With expert material selection, regular maintenance, and a trusted supplier, thermal power plants can continue to deliver reliable energy while keeping operational costs under control.
Looking for dependable refractory solutions for your thermal power plant? Contact our technical team today for custom recommendations, product samples, and installation support. Welcome to contact Xintai Refractory.