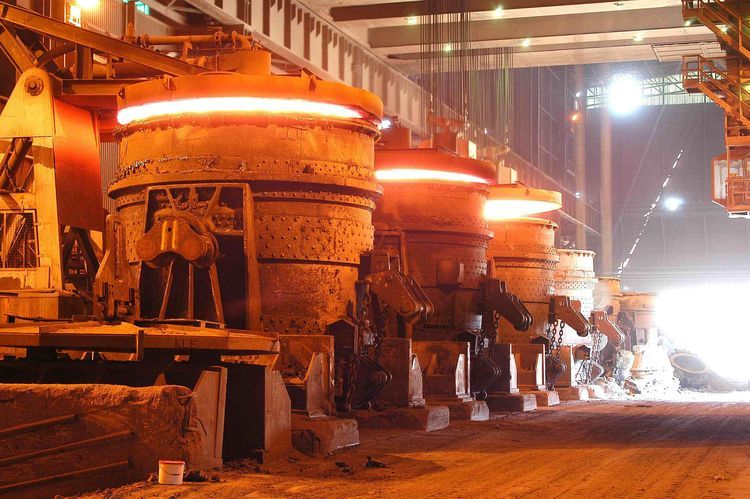
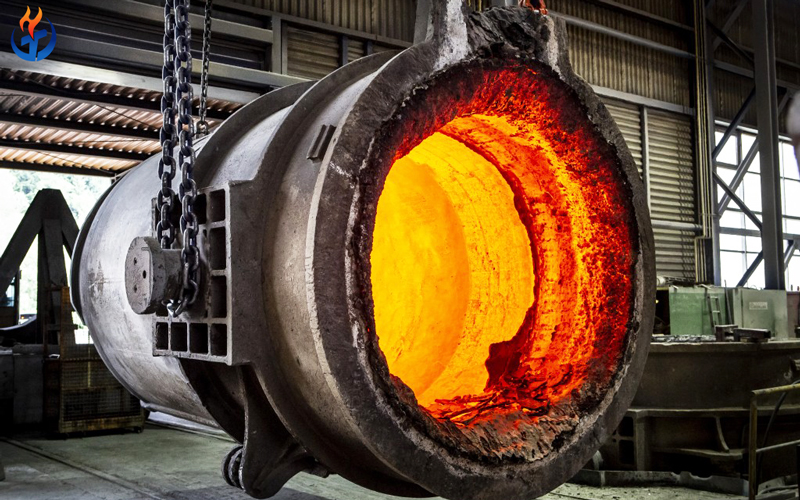
Steel production is a complex and energy-intensive process where every stage requires careful engineering and reliable materials. Among the critical equipment in steel plants, the steel ladle plays a vital role in holding, transporting, and refining molten steel before casting. To ensure safe operation and consistent steel quality, the refractory materials for steel ladles must be carefully selected and properly maintained.
The performance of ladle refractories directly influences productivity, energy consumption, and operational costs. A poorly designed or maintained lining can lead to premature failure, heat loss, contamination of steel, and even safety risks. In this article, we will explore the essential refractory materials used in ladles, their properties and advantages, maintenance strategies, and the best practices for maximizing ladle campaign life.

The Function of Refractory Materials in Steel Ladles
Steel ladles are exposed to some of the harshest conditions in the steelmaking process. The refractory lining must withstand:
High thermal loads: Molten steel temperatures often exceed 1600°C.
Thermal shock: Refractories must endure rapid heating and cooling cycles as ladles are preheated, filled, emptied, and cooled.
Corrosive slags: Steel refining slags contain aggressive oxides (CaO, FeO, SiO₂, MnO, etc.) that attack refractories.
Mechanical stress: Erosion from steel and slag movement, as well as impact from alloy additions, places mechanical strain on the lining.
Thus, the choice of refractory materials for steel ladles is not only about withstanding high temperatures but also about ensuring thermal shock resistance, chemical compatibility, and mechanical durability.
Types of Refractory Materials for Steel Ladles
Ladle refractories are engineered to meet different performance requirements depending on the zone of application. The lining is usually divided into working lining, permanent lining, and safety lining. Each zone requires tailored refractory solutions.
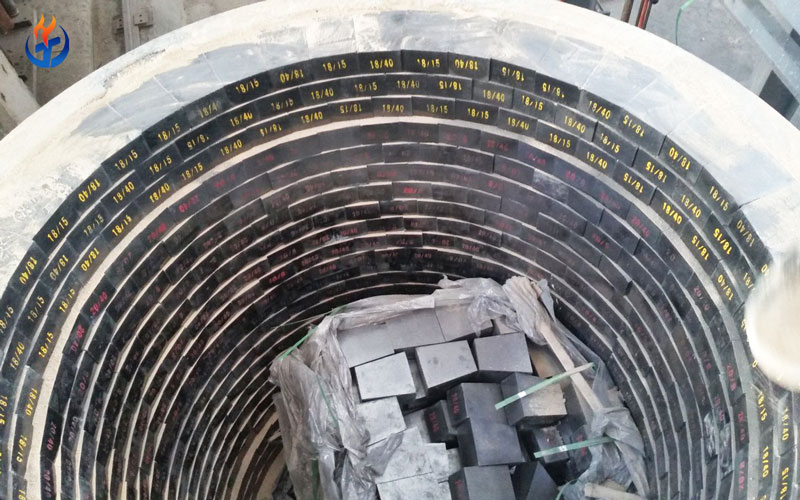
2.1 Ladle Refractory Bricks
Ladle refractory bricks form the backbone of ladle linings. These include:
High-alumina bricks: With Al₂O₃ content of 70% or higher, these bricks provide good resistance to corrosion and erosion. They are widely used in permanent linings.
Magnesia bricks: Offering superior resistance to basic slags, magnesia bricks are common in the slag zone.
Alumina-magnesia-carbon (AMC) bricks: A high-performance option combining alumina and magnesia with carbon, providing excellent slag resistance and thermal shock resistance.
Magnesia-carbon bricks: These are ideal for areas with high slag attack due to their carbon component, which improves resistance against penetration.
2.2 Alumina-Magnesia-Carbon Bricks (AMC Bricks)
Among all refractory materials for steel ladles, alumina-magnesia-carbon bricks are considered a breakthrough innovation. They are widely used in ladle linings, particularly in the slag line and impact zones, due to their outstanding properties:
Excellent thermal shock resistance: The carbon content minimizes spalling under frequent temperature changes.
Strong corrosion resistance: Magnesia provides high basicity resistance against CaO-rich slags.
Reduced steel contamination: Less risk of inclusion formation compared to some other bricks.
Longer service life: AMC bricks help extend ladle campaign lengths, reducing downtime.
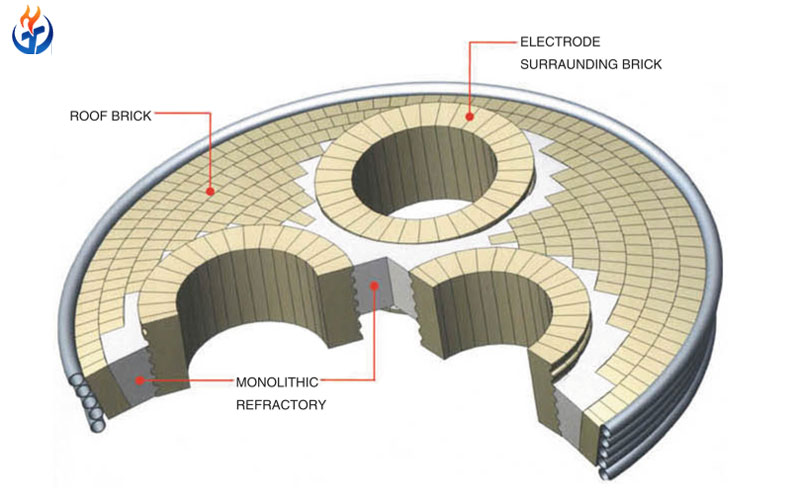
2.3 Monolithic Refractories
In addition to bricks, monolithic materials are used for repairs and specific ladle zones. These include:
Castables: Dense alumina-based castables for working linings.
Gunning materials: Used for hot repairs to extend ladle life.
Ramming masses: For critical joints and small repair applications.
The combination of ladle refractory bricks and monolithics ensures flexibility in design and maintenance.
Key Properties of Ladle Refractory Materials
To perform effectively, refractory materials for steel ladles must demonstrate the following properties:
High refractoriness: The ability to withstand steelmaking temperatures without melting or deforming.
Thermal shock resistance: Essential for surviving sudden heating and cooling cycles.
Slag resistance: Preventing penetration and corrosion from basic and acidic slags.
Mechanical strength: Withstanding erosion and impact.
Low porosity: Reducing slag and steel infiltration that weakens the lining.
The balance of these properties depends on the type of refractory selected and the operational practices of the steel plant.
Refractory Zoning in Steel Ladles
A typical steel ladle lining is divided into distinct zones, each requiring specific refractory solutions:
Bottom: Subject to mechanical erosion and thermal stress. Magnesia-carbon or alumina-based bricks are used.
Slag line: The most aggressive zone, attacked by slags and high temperatures. Alumina-magnesia-carbon bricks are ideal.
Sidewall: Experiences moderate thermal stress and slag splashing. High-alumina bricks or AMC bricks are commonly applied.
Impact zone (around the tap hole): Endures high turbulence and mechanical impact during steel pouring. Strong MgO-C or AMC bricks are preferred.
Permanent lining: Lower-cost high-alumina bricks protect the steel shell and provide structural stability.
By optimizing refractory material in each zone, steelmakers achieve longer ladle campaigns and reduced material consumption.
Maintenance of Ladle Refractory Linings
Even the best-designed refractory system requires careful maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Best practices include:
5.1 Regular Inspection
Routine checks help identify wear patterns, cracks, or hot spots early. Infrared thermography and endoscopy are often used to assess lining condition.
5.2 Hot Repairs
Using gunning and fettling materials, steel plants can repair worn areas while the ladle is still hot. This prevents unplanned shutdowns and extends ladle service life.
5.3 Slag Management
Controlling slag chemistry is crucial. By adjusting slag basicity, steelmakers can minimize refractory corrosion and reduce lining wear.
5.4 Thermal Shock Control
Preheating ladles before filling reduces thermal shock damage. Modern ladle preheaters help achieve consistent lining temperatures.
5.5 Campaign Planning
Strategically scheduling ladle relining, based on wear data and production cycles, ensures safe operation and cost efficiency.
Innovations in Ladle Refractory Materials
The steel industry continues to adopt new technologies to improve refractory performance. Recent developments include:
Improved AMC bricks with antioxidant additives (Al, Si, B₄C) to enhance oxidation resistance.
Eco-friendly refractories using recycled raw materials from spent ladle linings.
High-purity magnesia to reduce impurities and improve slag resistance.
Robotic gunning and repair systems for precise and safe maintenance.
Data-driven refractory management with digital monitoring of ladle lining wear.
These innovations are helping steel plants reduce refractory consumption, lower costs, and improve sustainability.
Choosing the Right Refractory Partner
Steel plants benefit greatly from working with reliable suppliers who offer:
High-quality ladle refractory bricks and AMC bricks tailored to specific conditions.
Technical expertise in installation, maintenance, and slag conditioning.
Customized solutions for unique operational needs.
After-sales support, including wear analysis and repair guidance.
A trusted partner ensures that steelmakers achieve maximum efficiency from their ladle operations.
Conclusion
The refractory materials for steel ladles are at the heart of efficient and safe steelmaking. From ladle refractory bricks to advanced alumina-magnesia-carbon bricks, each material is designed to provide thermal stability, slag resistance, and superior thermal shock resistance. Proper selection, combined with consistent maintenance practices, extends ladle campaign life, reduces downtime, and improves overall steel quality.
As steel production continues to evolve toward sustainability and cost optimization, innovation in ladle refractory technology will remain essential. By investing in high-performance refractories and proactive maintenance, steelmakers can secure long-term success in an increasingly competitive industry.
Contact Xintai today for expert consultation and premium refractory products that keep your steelmaking operations running smoothly and cost-effectively.