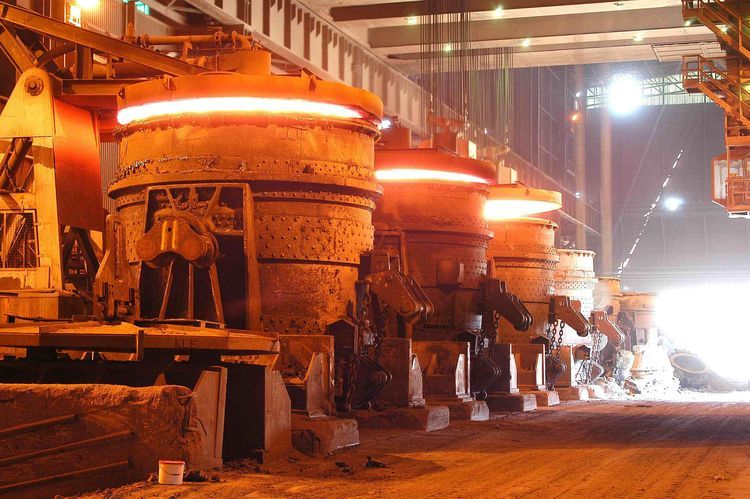
When it comes to building and maintaining a stable and efficient blast furnace, refractory materials play an irreplaceable role. Among them, blast furnace refractory bricks, fireclay bricks, and alumina bricks for ironmaking form the backbone of thermal protection and structural durability. These materials determine the furnace’s performance, energy efficiency, campaign life, and overall reliability during ironmaking operations.
Blast furnaces operate under some of the most extreme conditions in any industrial environment—high temperatures that exceed 2000°C, mechanical abrasion from descending burden materials, chemical erosion from slag, and rapid temperature fluctuations. Choosing the right refractory brick is therefore essential for operational stability and cost-effectiveness. This article explores the types of refractory bricks used in blast furnace applications, their characteristics, and the benefits they bring to iron and steel manufacturing.

Understanding the Role of Refractory Bricks in Blast Furnaces
A blast furnace is the heart of an integrated steel plant. Its lining must withstand the combined effects of thermal load, abrasion, chemical reactions, and mechanical pressure. Blast furnace refractory bricks protect the steel shell from thermal damage and enable continuous, long-term iron production. They insulate the inner chamber, maintain thermal stability, and create the ideal environment for efficient ironmaking.
Different zones of the blast furnace—including the throat, shaft, belly, bosh, tuyere area, and hearth—require different refractory materials. No single brick type can meet all the requirements. This is why material selection is strategic and highly specific.
Main Types of Refractory Bricks for Blast Furnace Applications
Refractory bricks for blast furnace lining can be divided into several key categories based on their composition, thermal properties, and application areas.
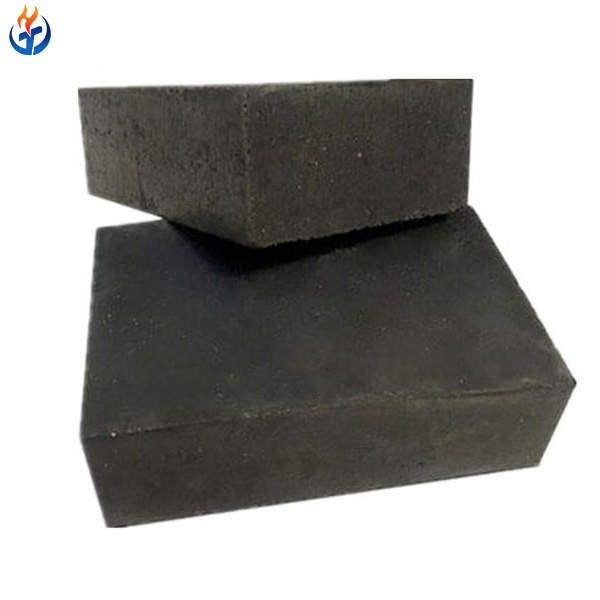
2.1 Fireclay Bricks
Fireclay bricks are one of the oldest and most widely used refractory materials. They are made primarily from chamotte, clay, and a controlled amount of alumina.
Characteristics of Fireclay Bricks
Alumina content typically ranges from 30–48%.
Good thermal shock resistance.
Moderate refractoriness and load-bearing capacity.
Economical and versatile.
Where Fireclay Bricks Are Used in Blast Furnaces
Fireclay bricks are commonly used in:
Furnace stacks
Upper shaft areas
Iron trough linings
Coke ovens associated with blast furnace operations
Their balance of cost and performance makes them ideal for zones with moderate temperatures and less severe corrosion.
2.2 High Alumina Bricks for Ironmaking
Alumina bricks for ironmaking contain alumina levels from 55% all the way up to 90%, depending on the grade. These high alumina bricks offer excellent performance in the intense conditions of a blast furnace’s mid to lower sections.
Properties of High Alumina Bricks
High refractoriness and load softening temperature.
Superior resistance to slag attack.
Excellent abrasion resistance.
High mechanical strength.
Applications in the Blast Furnace
High alumina bricks are widely used in:
Furnace belly and bosh areas
Tuyere region exposed to high temperatures
Carbon-rich and slag-rich zones
Hot blast stoves used alongside the furnace
These bricks are preferred for their ability to withstand rapid chemical and thermal stress.
2.3 Silicon Carbide Bricks
Silicon carbide (SiC) bricks are known for their exceptional strength and abrasion resistance.
Key Advantages
Extremely high thermal conductivity.
Superior slag corrosion resistance.
Excellent resistance to thermal shock.
High mechanical strength even at elevated temperatures.
Applications
SiC bricks are often used in:
Hearth and tuyere zones
Furnace linings exposed to high mechanical wear
Slag runner and iron runner systems
Because of their strength and erosion resistance, they significantly extend furnace campaign life.
2.4 Carbon Bricks and Graphite Bricks
Carbon-based bricks are essential for modern blast furnace hearths.
Why Carbon Bricks Are Critical
Outstanding resistance to molten iron and slag.
Extremely low wettability, preventing metal penetration.
High thermal conductivity to reduce lining stress.
Ability to withstand very high temperatures without deformation.
Typical Uses
Blast furnace hearth bottom
Hearth sidewalls
Bottom plates and cooling brick interfaces
These bricks help ensure long refractory life in the most demanding operating area of a blast furnace.
2.5 Silica Bricks
Silica bricks are known for their excellent volume stability at high temperatures.
Properties
Over 93% SiO₂ content.
Exceptional resistance to creep.
Ability to retain structural integrity under prolonged high-temperature exposure.
Applications
Silica bricks are used in:
Furnace roof structures
Hot blast stoves
Combustion chambers
Their dimensional stability prevents structural deformation under continuous heat load.
Factors That Affect Refractory Selection for Blast Furnaces
Selecting the right refractory brick for each section of the blast furnace requires considering multiple factors:
3.1 Temperature Profile
Different parts of the furnace experience different maximum temperatures.
For example:
Shaft region: lower temperature, suitable for fireclay bricks.
Bosh and tuyere area: highest temperature, requiring high alumina or SiC bricks.
3.2 Chemical Attack
Slag type, iron composition, and chemical gases influence the corrosion rate of different refractory materials.
3.3 Erosion and Abrasion
Mechanical wear from descending burden materials affects the shaft and belly region, calling for bricks with strong abrasion resistance.
3.4 Thermal Shock Cycles
Operation fluctuations and hot-cold cycles demand materials with excellent thermal shock resistance.
3.5 Installation and Maintenance
Some bricks are easier to install, repair, or replace, which impacts overall maintenance planning.
Benefits of Using High-Quality Refractory Bricks in Blast Furnaces
Whether using fireclay bricks, alumina bricks for ironmaking, or advanced carbon and SiC bricks, high-quality refractory materials provide significant operational advantages.
4.1 Improved Furnace Efficiency
Efficient refractory linings:
Reduce heat loss.
Maintain stable internal temperatures.
Improve fuel efficiency.
Enhance overall productivity.
A well-insulated furnace consumes less energy to reach the same output.
4.2 Longer Furnace Campaign Life
High-performance refractory bricks withstand erosion, wear, and heat stress over long periods. This leads to:
Fewer shutdowns.
Reduced maintenance costs.
Higher operational availability.
Campaign life is one of the most important KPIs for ironmaking operations.
4.3 Enhanced Safety
Stable refractory linings prevent:
Shell overheating
Breakouts of hot metal
Furnace deformation or collapse
Reliability is essential in heavy industry environments, where failure can result in major losses.
4.4 Reduced Slag and Metal Penetration
Carbon bricks and high-alumina bricks resist penetration by molten metal and slag. This protects the furnace’s structural integrity and prevents premature lining failure.
4.5 Better Resistance to Thermal Shock
Thermal shock resistance is crucial for regions exposed to rapid temperature fluctuations. High-grade refractory materials ensure that the lining can handle sudden changes without cracking.
4.6 Lower Operational Costs
Although high-quality refractory bricks may come with a higher upfront cost, they significantly reduce:
Fuel consumption
Downtime
Repair frequency
Personnel and equipment maintenance needs
This leads to long-term financial benefits.
Conclusion
Refractory bricks are essential materials for blast furnace performance, durability, and safety. Whether using blast furnace refractory bricks, versatile fireclay bricks, or high-performance alumina bricks for ironmaking, choosing the proper material ensures long-term reliability and efficiency.
Different furnace zones require tailored refractory solutions—silica bricks for upper structures, fireclay bricks for moderate-temperature areas, high alumina bricks for the belly and bosh, and carbon or SiC bricks for the hearth and tuyere region. Together, they support stable thermal conditions and protect the furnace shell from extreme heat and chemical attack.
By understanding the specific properties and benefits of each type of refractory brick, iron and steel manufacturers can maximize productivity, minimize downtime, and extend the overall service life of their blast furnaces.
If you’re designing or maintaining a kiln, furnace, or high-temperature unit, contact Xintai Refractory today. Our experts will help you choose the right refractory brick dimensions and materials for optimal performance and longevity.
Email: sales@xintairefractory.com
Website: www.xintairefractory.com