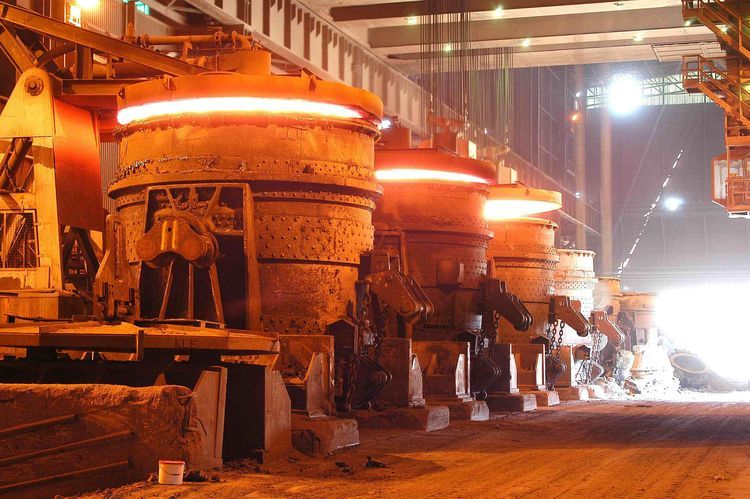
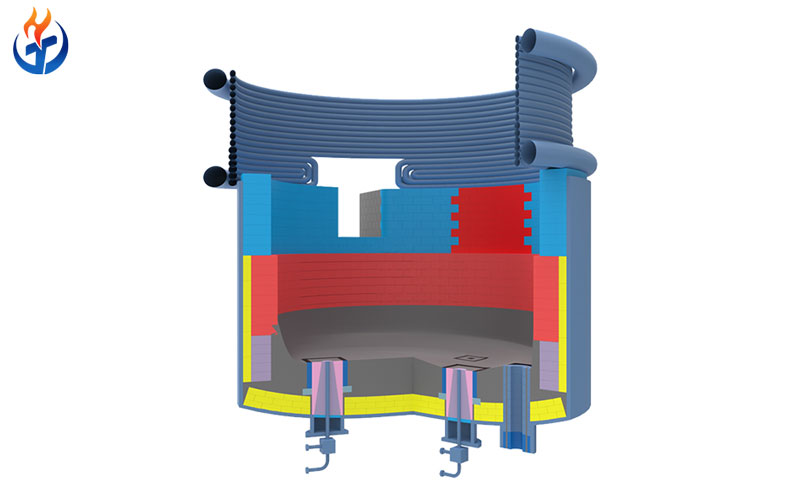
Electric arc furnaces (EAFs) operate under extremely harsh conditions, including ultra-high temperatures, intense thermal shock, chemical corrosion from slag and molten steel, mechanical abrasion, and strong electromagnetic and arc radiation. As a result, the selection of refractory materials for electric furnaces plays a decisive role in furnace performance, operational stability, energy efficiency, and overall service life.
Modern electric furnace refractory systems are no longer based on a single material. Instead, they are composed of a complete set of specialized refractory products designed for different furnace zones and operating conditions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the main types of refractory materials for electric arc furnaces, their structural characteristics, performance advantages, and typical applications.
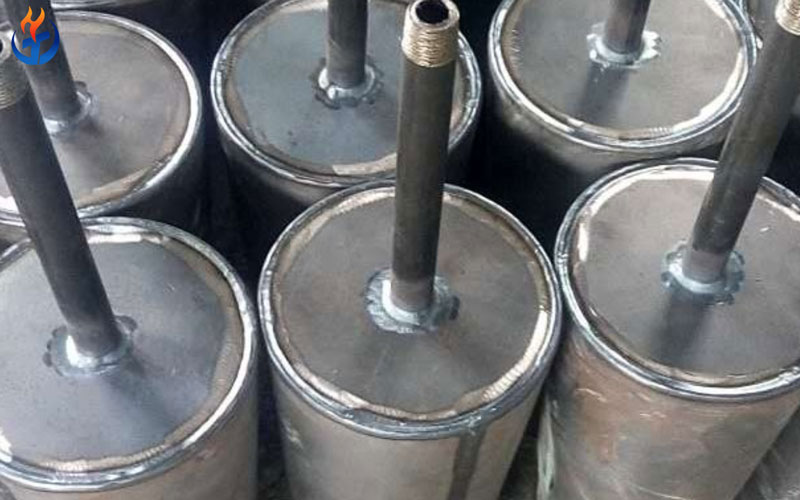
1. Electric Furnace Purging Plugs
Electric furnace purging plugs are typically designed as metal tube–magnesia carbon brick composite structures. Their primary function is to ensure stable and efficient bottom stirring or combined top-and-bottom blowing during electric arc furnace steelmaking.
Structural Characteristics
The gas channels are constructed from heat-resistant stainless steel tubes, commonly with dimensions of φ3×1 mm or φ4×1 mm, ensuring reliable gas delivery under high-temperature conditions.
Depending on the plug size and furnace design, each purging plug may contain between 10 and 100 stainless steel tubes, providing sufficient gas flow capacity.
The matrix material consists of a high-quality magnesia carbon brick, allowing the purging plug to achieve a service life synchronized with that of the furnace bottom lining.
Performance Advantages
High gas permeability with uniform and stable airflow distribution
Excellent blowing efficiency under properly controlled operating conditions
Reliable performance for EAF combined top-and-bottom blowing processes
Strong resistance to thermal shock and molten steel erosion
Due to the high number of metal tubes and the optimized internal layout, electric furnace purging plugs deliver high gas blow-through rates and consistent stirring performance, making them indispensable components in modern electric arc furnace bottom systems.

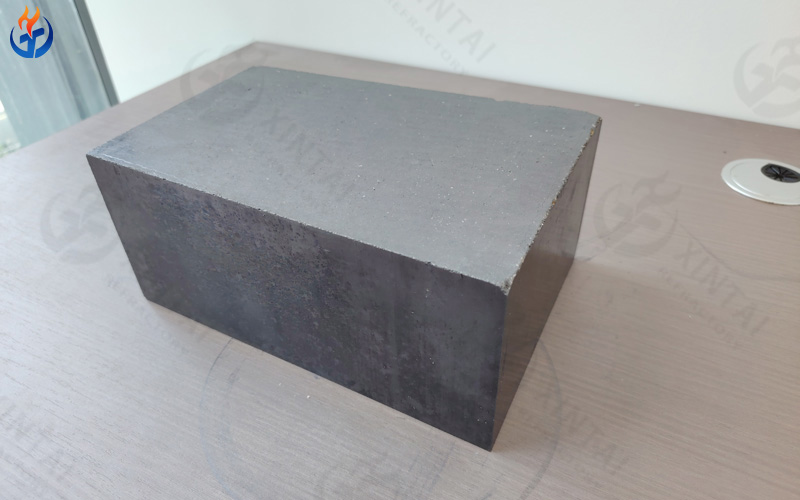
2. Magnesia Carbon Bricks for Electric Furnaces
Magnesia carbon bricks are among the most widely used refractory materials for electric arc furnaces. They are carefully engineered according to different furnace zones and operating environments.
Raw Material Composition
High-purity, high-density fused magnesia
Large-crystal fused magnesia
High-purity graphite
Appropriate amounts of metallic antioxidants
Phenolic resin as the bonding agent
Key Properties
Excellent resistance to slag corrosion
Strong resistance to thermal shock
High mechanical strength at elevated temperatures
Low wettability with molten steel and slag
Different grades of magnesia carbon bricks are selected for various furnace positions, such as furnace walls, slag lines, and hearth zones, based on specific metallurgical conditions. Their balanced performance makes them a cornerstone of EAF refractory lining systems.

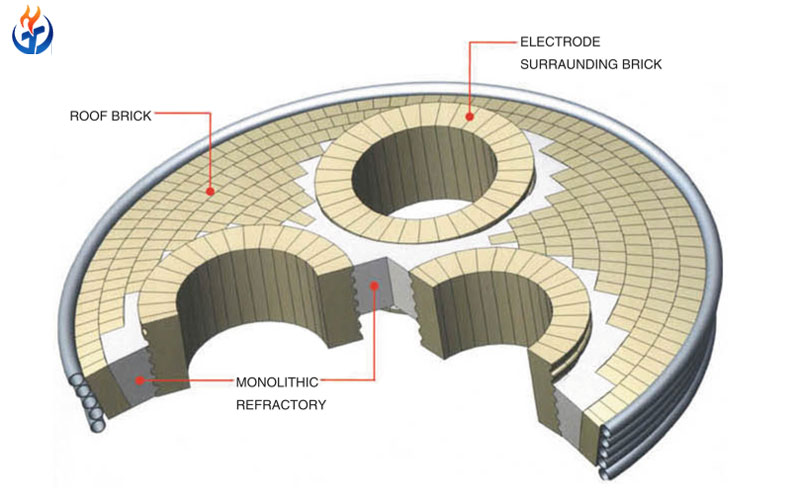
3. Electric Furnace Roof and Ladle Refining Furnace Roof Refractories
Electric furnace roofs and refining furnace roofs are exposed to some of the most aggressive conditions in steelmaking operations.
Operating Challenges
Frequent and severe thermal shock
Chemical corrosion from slag and furnace gases (CO, CO₂, SO₂)
Intense radiation from high-temperature electric arcs
High-speed gas flow erosion caused by dust extraction systems
Material Design Concept
To meet these challenges, roof refractories are formulated using:
Cement-bonded or non-cement bonded systems
Ultrafine powder technology
High-performance binders and chemical additives
Scientifically optimized particle size distribution
Each formulation is precisely adjusted according to the furnace type, power level, and operating conditions.
Performance Characteristics
Outstanding thermal shock resistance
Strong resistance to slag and gas corrosion
Excellent volume stability
Extended service life
The PN series electric furnace and refining furnace roof products manufactured by Puyang Refractories are suitable for:
Conventional EAFs
Ultra-high power (UHP) electric arc furnaces
Ladle refining furnaces
VD (Vacuum Degassing) furnaces
4. Electric Furnace Tapping Spouts
The tapping spout is a critical component in electric furnace steelmaking, directly affecting tapping safety and efficiency.
Material Structure
Large-crystal fused magnesia
High-purity graphite
Metallic antioxidants
Phenolic resin binder
Manufacturing Methods
Cold isostatic pressing (for integral tapping spouts)
Mechanical pressing (for segmented tapping spouts)
Key Advantages
Excellent oxidation resistance
High mechanical strength
Strong resistance to steel and slag erosion
Easy replacement and maintenance
Long service life
These tapping spouts are designed to withstand repeated thermal cycles and aggressive molten steel flow without premature failure.
5. Tapping Hole Filling Materials
Tapping hole filling materials play a vital role in ensuring automatic tapping and preventing molten steel leakage during EAF operations.
Working Principle
During smelting, the filling material in contact with molten steel forms a sintered layer, effectively blocking steel penetration.
Beneath the sintered layer, the unsintered material remains loose.
When the slide gate is opened for tapping, the loose material flows out smoothly.
Under steel pressure, the sintered layer breaks, enabling automatic opening of the tapping hole.
Performance Features
Non-floating behavior
High automatic opening rate
Simple operation
Safe use
No contamination of molten steel
These materials are widely used in electric furnace tapping systems and contribute significantly to operational safety and efficiency.
6. Dry Ramming Mix for Electric Furnace Bottoms
Dry ramming mixes are specially developed for HP and UHP electric furnace bottoms, where resistance to molten steel penetration and erosion is critical.
Design Principles
Based on the principle of maximum particle packing density
Made from high-quality synthetic raw materials
Combined with specialized additives and binders
Advantages
Strong resistance to molten steel infiltration
Excellent erosion resistance
Easy sintering during operation
High bulk density after ramming
Convenient and efficient installation
Dry ramming mixes provide a dense and durable furnace bottom lining, contributing to stable furnace performance and reduced maintenance frequency.
7. Electric Furnace Gunning Repair Materials
Gunning repair materials are designed for both cold and hot repairs of electric furnace linings.
Raw Materials and Composition
High-quality magnesia
Magnesia-calcia materials
Dolomite
Unique binders and additives
Performance Characteristics
High adhesion strength
Low rebound rate during spraying
Easy sintering
Strong resistance to scouring and erosion
Excellent corrosion resistance
These materials are ideal for quick and effective repairs of furnace walls, slag lines, and other critical areas, minimizing downtime and extending lining life.

8. Hot Repair Materials for Tapping Spouts and Furnace Bottoms
Hot repair materials are essential for localized hot-state maintenance during EAF steelmaking operations.
Typical Applications
Filling gaps between sleeve bricks and furnace bottoms when replacing tapping spouts
Repairing localized pits or cracks in furnace bottoms without cooling down the furnace
Material Characteristics
Made from high-iron, high-calcium magnesia raw materials
Combined with unique organic binders
Key Benefits
Rapid strength development at low temperatures
High strength at elevated temperatures
Excellent resistance to scouring and corrosion
These hot repair materials allow steel plants to perform efficient maintenance without interrupting production cycles.
Conclusion
The refractory materials used in electric arc furnaces form a highly integrated system, where each product serves a specific function under extreme operating conditions. From gas permeable bricks and magnesia carbon bricks to furnace roofs, tapping spouts, ramming mixes, and repair materials, every refractory component contributes to furnace efficiency, safety, and longevity.
Selecting the right refractory materials for electric furnaces requires not only an understanding of material properties but also a deep knowledge of steelmaking processes and operating conditions. By using well-designed, application-specific refractory solutions, steel producers can significantly improve furnace performance, reduce refractory consumption, and achieve more stable and cost-effective operations.