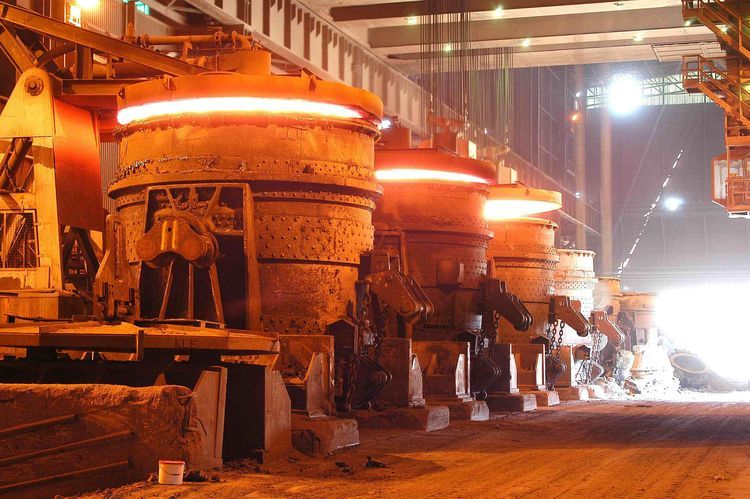
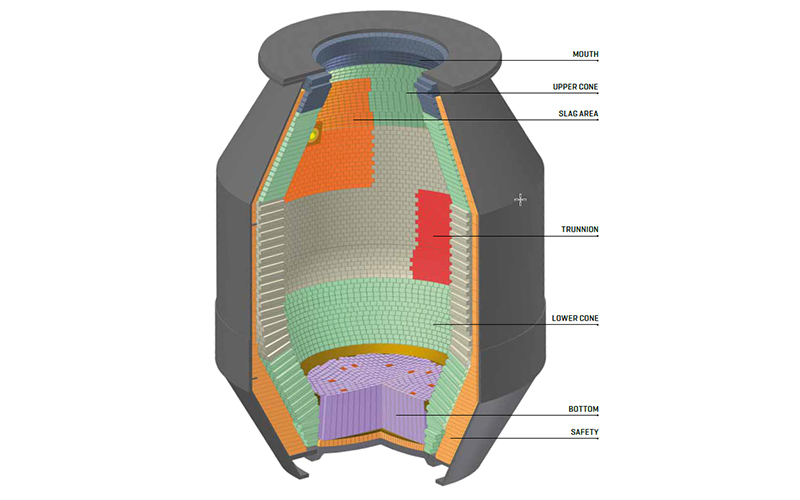
In basic oxygen steelmaking (BOF), the converter operates under extremely harsh conditions characterized by ultra-high temperatures, intense mechanical erosion, strong chemical corrosion from molten steel and slag, and frequent thermal cycling. Refractory materials used in converters play a decisive role in operational stability, steel quality, production efficiency, and overall furnace campaign life.
The converter refractory materials series is designed to meet the diverse functional requirements of different furnace zones, including the furnace bottom, sidewalls, trunnion area, slag line, tapping zone, and maintenance areas. These products directly contact molten steel and slag, demanding superior strength, excellent slag resistance, high refractoriness, and outstanding thermal shock stability.
Based on different metallurgical conditions and wear mechanisms, various grades and structures of refractory products are selected and combined to achieve optimal furnace performance and extended service life.
This article provides a comprehensive introduction to the main refractory materials used in converters, including permeable bricks, magnesia-carbon bricks, tapping hole products, slag control materials, repair materials, ramming mixes, and slag-stopping systems.
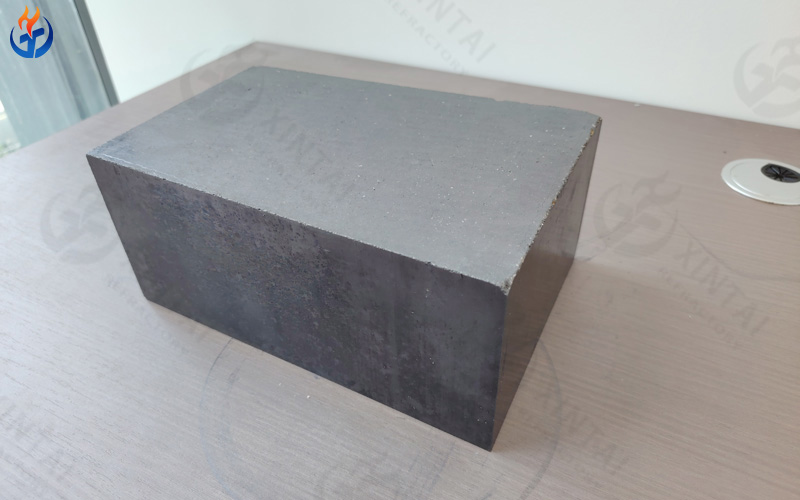
Converter Magnesia Carbon Bricks
Converter magnesia carbon bricks are the core lining materials for most converter zones. They are specifically designed according to different operating positions and metallurgical environments within the converter.
Raw Materials and Manufacturing Process
High-purity, high-density fused magnesia
Large-crystal electrofused magnesia
High-purity graphite
Appropriate antioxidant additives
Phenolic resin as the bonding agent
High-pressure forming technology
Key Properties
High refractoriness under load
Strong resistance to slag corrosion and steel penetration
Excellent thermal shock resistance
Good mechanical strength at high temperatures
Controlled oxidation behavior due to antioxidants
By adjusting graphite content, magnesia purity, and antioxidant formulations, different grades of magnesia carbon bricks can be tailored for slag line zones, working linings, trunnion areas, and furnace bottoms. This zoned application strategy ensures optimal cost-performance balance and maximizes lining life.

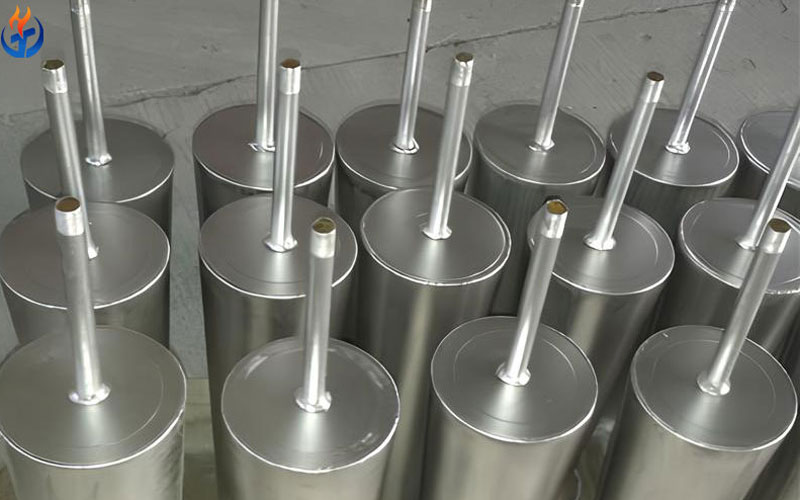
Converter Purging Plug
Converter purging plugs are key functional refractory products used in bottom blowing systems. These products are metal-tube–magnesia carbon composite structures specifically designed to support efficient and stable gas injection during converter steelmaking.
Structural Characteristics
Gas channels are constructed from heat-resistant stainless steel tubes (φ3×1 mm or φ4×1 mm).
Depending on the purging plug size and application position, the number of stainless steel tubes typically ranges from 10 to 100.
The plug matrix is manufactured from high-quality magnesia-carbon refractory material, ensuring compatibility with the converter bottom lining.
Performance Advantages
High gas permeability and stable airflow ensured by multiple gas channels
Excellent blowing efficiency under proper operating conditions
Service life synchronized with the converter bottom lining
Reliable performance for combined top and bottom blowing processes
The use of stainless steel gas tubes provides strong structural integrity and excellent resistance to high-temperature oxidation. With proper operation and maintenance, converter purging plugs achieve high gas blow-through rates and stable airflow, significantly enhancing molten bath stirring efficiency and improving metallurgical reaction kinetics.

Converter Tapping Hole Products
The converter tapping hole is one of the most critical and vulnerable parts of the furnace, subjected to severe erosion, oxidation, and thermal shock during tapping operations.
Material Composition
High-purity fused magnesia or large-crystal magnesia
High-purity graphite
Unique antioxidant system
Phenolic resin bonding
Forming Methods
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) for integral tapping holes
Mechanical pressing for segmented tapping hole designs
Product Advantages
Excellent oxidation resistance
High mechanical strength
Strong resistance to molten steel and slag erosion
Easy installation and replacement
Long service life
These tapping hole products ensure smooth steel tapping operations, reduce maintenance frequency, and contribute to stable steel quality.
Application Characteristics of Converter Lining Materials
All converter refractory materials products are applied in lining areas that directly contact molten steel and slag. They share several essential performance requirements:
High strength under thermal and mechanical loads
Strong slag resistance
Good thermal shock stability
High refractoriness
Adaptability to different smelting conditions
Based on steel grade, slag composition, blowing intensity, and production rhythm, different grades of magnesia carbon bricks and functional materials are selected for each converter zone to ensure optimal furnace performance.
Slag Forming Balls
Slag forming balls are auxiliary refractory products mainly used for slag splashing furnace protection during converter steelmaking.
Raw Materials and Function
Light-burned magnesia
Magnesite powder
Press-formed structure after mixing
Main Purpose
Improve slag splashing efficiency
Promote uniform slag coating on furnace lining
Enhance furnace lining protection
Extend converter service life
By improving slag viscosity and adhesion, slag forming balls play a significant role in extending furnace campaigns and reducing refractory consumption.
Slag Stopping Balls
During converter tapping, when the molten steel level drops below a critical height, a vortex tends to form above the tapping hole. This vortex can easily entrain slag into the ladle, negatively affecting steel cleanliness.
Working Principle
After slag stopping balls are added:
The vortex pushes the ball toward the tapping hole
The ball blocks slag entry into the ladle
Molten steel continues flowing through the gap between the ball and tapping hole
Benefits
Significantly reduces slag carryover
Improves steel quality
Enhances ladle lining life
Stabilizes downstream refining processes
Slag Stopping Plugs
Slag stopping plugs serve the same purpose as slag stopping balls but offer improved placement accuracy.
Structural Design
Consists of a plug head and guiding rod
Plug head material is similar to slag stopping balls
Guided insertion ensures higher hit rate
Application Advantages
Higher success rate compared to slag stopping balls
More reliable slag blocking effect
Easy operation using slag stopping vehicles
This product has been successfully applied in major steel plants such as Shagang, Huaigang, and Hongyang, demonstrating stable and reliable performance.
Converter Large Area Repair Materials
Converter large area repair materials are specifically developed for early damage areas such as trunnion zones, large wall surfaces, and around the tapping hole.
Material Features
High-quality magnesia-based raw materials
Special organic binders
Low smoke emission
High bonding strength
Excellent high-temperature fluidity
Strong erosion and scouring resistance
Working Mechanism
At high temperatures, the repair material rapidly softens and becomes fluid. After charging and furnace rocking:
The material spreads evenly over damaged areas
Forms a uniform thickened lining layer
Rapidly sinters and bonds with the original lining
This process effectively restores lining thickness and significantly extends furnace service life.
Converter Gunning Repair Materials
Converter gunning repair materials are formulated based on spraying construction characteristics and converter steelmaking process requirements.
Composition and Properties
High-quality magnesia and magnesia-calcia raw materials
Special binders and additives
High adhesion strength
Low rebound rate
Easy sintering
Excellent resistance to erosion and scouring
Application Scope
Cold and hot repair of converter linings
Suitable for various furnace zones
These materials are ideal for fast, efficient maintenance operations, helping steel plants reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Magnesia-Alumina Ramming Mixes
Magnesia-based and magnesia-alumina ramming mixes are widely used in converter bottom and tapping zone construction.
Key Characteristics
Made from fused magnesia and additives
Strong resistance to erosion and scouring
Convenient installation
Stable performance under high temperatures
They are suitable for ramming construction around the furnace bottom and tapping hole, ensuring dense structures and long service life.
Alumina-Magnesia Ramming Mixes
Alumina-magnesia ramming mixes are designed for applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance.
Raw Materials and Applications
Corundum
Fused magnesia
Additives for improved workability
Typical Uses
Filling gaps around ladle bottom seating bricks
Filling gaps around tundish seating bricks
Furnace mouth casting construction
These materials offer excellent resistance to slag erosion and thermal shock while maintaining easy installation.
Converter Sliding Plate Slag Stopping Systems
Sliding plate slag stopping systems are critical components for precise slag control during tapping.
Material Types
Alumina-carbon sliding plates
Alumina-zirconia-carbon sliding plates
Zirconia-inserted sliding plates
Performance Advantages
High mechanical strength
Strong resistance to molten steel scouring
Excellent corrosion resistance
Superior thermal shock stability
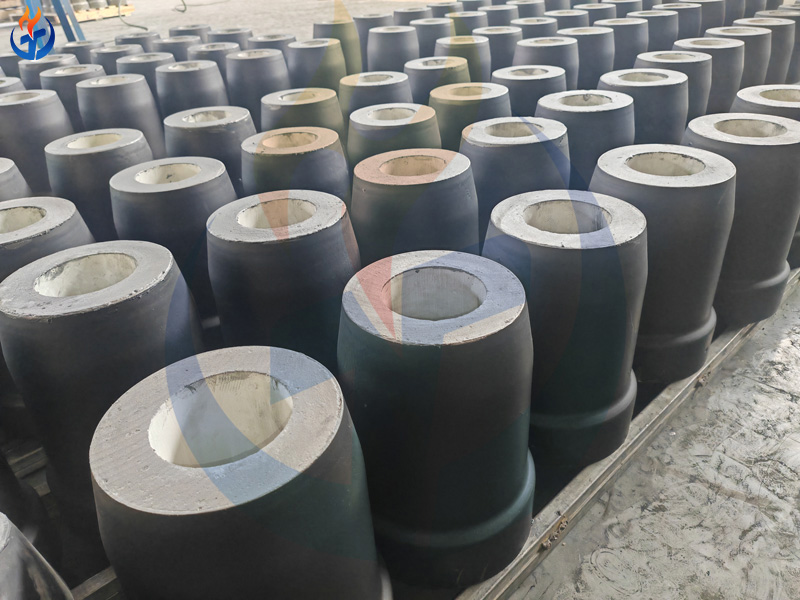
Outer Nozzle Bricks
Outer nozzle bricks are essential components in converter tapping systems.
Material Classification
Magnesia-carbon
Alumina-carbon
Alumina-zirconia-carbon
Manufacturing Process
High-tonnage press forming
Low-temperature treatment or high-temperature firing
Key Benefits
High strength
Excellent scouring resistance
Strong corrosion resistance
Good thermal shock stability

Conclusion
The converter refractory materials series forms a complete and integrated system that supports stable, efficient, and long-life converter steelmaking operations. From working linings and functional bricks to slag control products and repair materials, each product plays a critical role in optimizing furnace performance and steel quality.
By selecting appropriate refractory materials based on specific furnace zones and metallurgical conditions, steel plants can significantly extend converter service life, reduce refractory consumption, improve production stability, and achieve better economic and technical results.
As converter steelmaking technology continues to evolve toward higher efficiency, lower emissions, and longer furnace campaigns, high-performance refractory materials will remain a cornerstone of sustainable steel production.