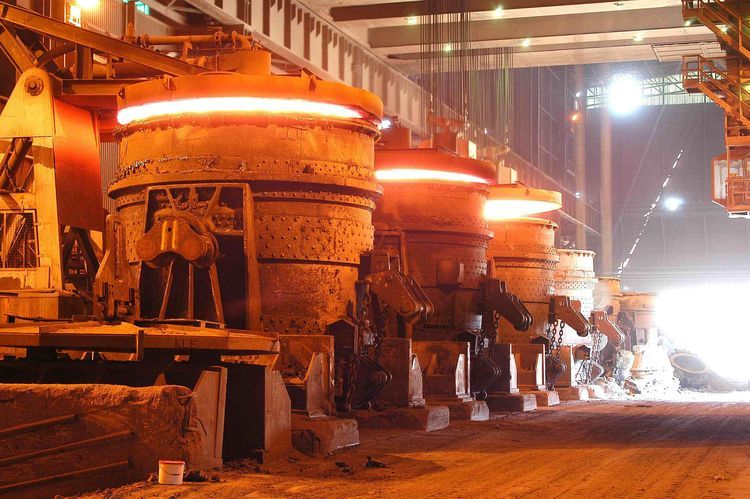
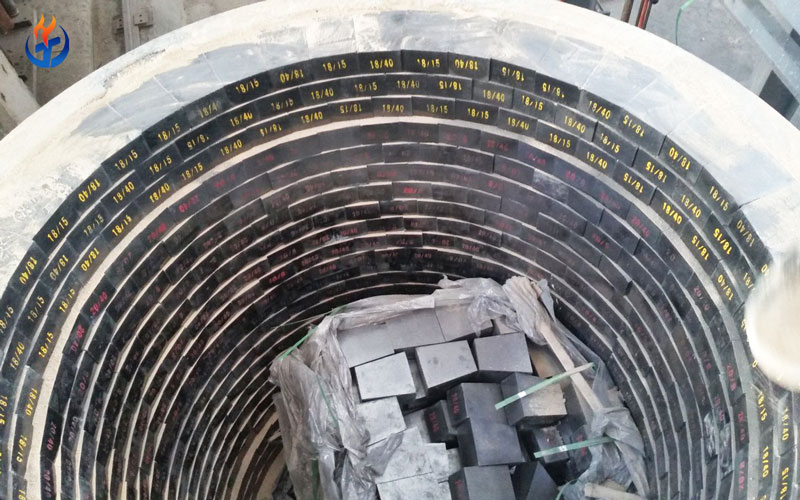
In the ceramic, metallurgy, and refractory industries, the performance and efficiency of a kiln depend heavily on the quality of its refractory lining. Among the various types of kilns, intermittent kilns—also known as periodic kilns—are widely used for firing ceramics, clay bricks, lime, and other materials in batches. The temperature cycle and frequent heating-cooling operations demand highly stable and reliable refractory materials.
This is where intermittent kiln refractory brick plays a crucial role, ensuring structural integrity, thermal insulation, and long service life under repeated thermal shocks.

Understanding the Intermittent Kiln
An intermittent kiln operates in cycles: loading, heating, soaking, cooling, and unloading. Unlike continuous kilns, intermittent kilns stop between firing cycles, leading to significant thermal fluctuations. These temperature variations cause expansion and contraction in the kiln structure, creating thermal stress in the refractory lining.
For this reason, the selection of intermittent kiln refractory materials—including refractory bricks, castables, and insulating linings—is critical to maintaining performance, minimizing heat loss, and extending service life.
Requirements for Intermittent Kiln Refractory Brick
Refractory bricks used in intermittent kilns must meet several performance requirements due to frequent temperature changes and mechanical stress:
Excellent thermal shock resistance: To withstand repeated heating and cooling without cracking or spalling.
High refractoriness: The ability to maintain strength and shape at temperatures up to 1600°C or higher.
Low thermal conductivity: To reduce energy loss and maintain consistent firing temperatures.
Good structural strength: Ensuring that the brickwork remains intact during expansion and contraction.
Chemical resistance: Protection from gases, vapors, or slag produced during the firing process.
The performance of an intermittent kiln refractory brick depends on its composition, manufacturing process, and installation quality.
Common Types of Refractory Bricks Used in Intermittent Kilns
Depending on the kiln temperature, atmosphere, and product type, different refractory brick grades are selected for the lining. Below are the most commonly used bricks in intermittent kilns:
(1) Fire Clay Bricks
Main component: 30–45% Al₂O₃
Working temperature: Up to 1400°C
Features: Good thermal shock resistance, easy to install, economical.
Applications: Kiln wall, arch, and combustion chamber of small to medium intermittent kilns.
Fire clay bricks are one of the most widely used intermittent kiln refractory bricks due to their balance between cost and durability.
(2) High Alumina Bricks
Main component: Al₂O₃ ≥ 48%
Working temperature: 1500–1700°C
Features: High refractoriness, strong resistance to slag and wear, suitable for high-temperature zones.
Applications: Roof and flame zone of ceramic or refractory firing kilns.
(3) Mullite Bricks
Main component: 70–80% Al₂O₃ with mullite phase.
Working temperature: Up to 1750°C
Features: Excellent high-temperature strength, low thermal expansion, and superior thermal shock resistance.
Applications: High-temperature sections, flame-impinged zones, and kiln arches.
(4) Insulating Fire Bricks (IFB)
Main component: Lightweight clay or mullite.
Features: Low bulk density, very low thermal conductivity, but limited mechanical strength.
Applications: Back lining or insulation layer behind dense bricks to reduce heat loss.
Intermittent Kiln Refractory Castables and Castable Lining
In addition to bricks, intermittent kiln refractory castables are widely used for parts that require complex shapes or monolithic construction. Castables are unshaped refractories that can be cast, pumped, or gunned into place, forming a seamless lining after curing and sintering.
Advantages of Castable Linings:
Fewer joints than brick linings, reducing the risk of gas leakage and erosion.
Easier installation in irregular or curved kiln sections.
Repairable in situ without dismantling large areas of the lining.
Lower thermal conductivity for better energy efficiency.
Common Castable Types for Intermittent Kilns:
High Alumina Castable: For working linings up to 1600°C.
Mullite Castable: For zones exposed to high thermal stress and flame impact.
Insulating Castable: For backup insulation layer.
Low Cement Castable (LCC): Offers superior strength and thermal shock resistance compared to conventional types.
A combination of intermittent kiln refractory brick and refractory castable lining provides the best balance between mechanical strength, thermal insulation, and installation flexibility.
Typical Refractory Structure Design for Intermittent Kilns
A well-designed refractory structure can improve energy efficiency and extend kiln life. The general structure includes:
| Kiln Section | Recommended Refractory | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Roof/Arch | High alumina or mullite bricks | High-temperature strength, flame resistance |
| Side Walls | Fire clay or high alumina bricks + insulating layer | Structural support + thermal insulation |
| Kiln Bottom | Dense fire clay bricks or castable | Mechanical load bearing |
| Combustion Chamber | Mullite bricks or LCC castable | Flame impact resistance |
| Insulation Layer | Lightweight insulating bricks or castable | Reduce heat loss |
For small batch ceramic kilns or laboratory kilns, an all-castable lining may be used for simplified maintenance and improved heat retention.
Choosing the Right Supplier for Intermittent Kiln Refractories
Selecting a reliable refractory supplier is as important as choosing the material itself. A professional manufacturer provides not only quality materials but also technical guidance in design, installation, and after-service.
When choosing an intermittent kiln refractory supplier, consider:
Over 20 years of experience in refractory manufacturing.
Comprehensive product range: fire clay bricks, high alumina bricks, mullite bricks, insulating bricks, and castables.
Proven performance in ceramics, steel, cement, and non-ferrous metal industries.
Custom engineering solutions for different kiln types and firing temperatures.
A trusted partner can help you design a cost-effective and energy-efficient refractory system tailored to your production needs.
Conclusion
The performance of an intermittent kiln depends largely on its refractory lining. High-quality intermittent kiln refractory bricks and castable linings not only ensure structural stability but also improve firing efficiency and reduce energy costs.
By combining suitable materials—such as fire clay, high alumina, and mullite bricks—with insulating castables, operators can achieve a durable, thermally stable, and easy-to-maintain kiln lining system. Whether you are building a new kiln or relining an existing one, investing in premium refractory materials is the foundation for long-term success.
Reach out to Xintai Refractory today for professional guidance and premium mullite refractory bricks, designed to enhance your ceramic kiln lining with reliable performance, improved energy efficiency, and extended service life.