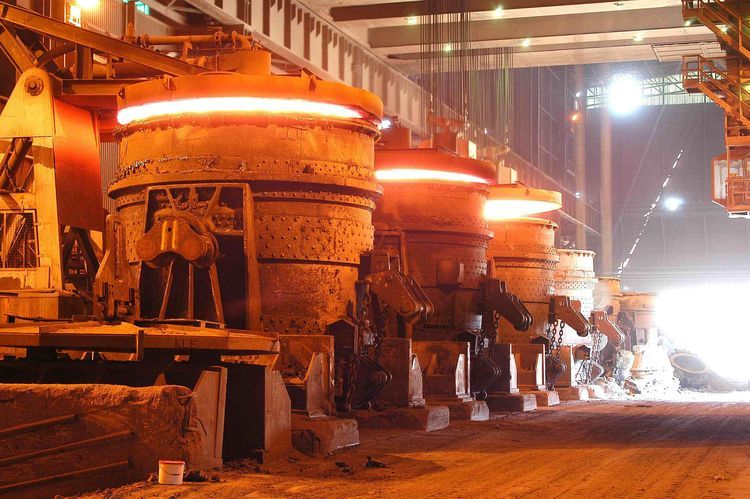
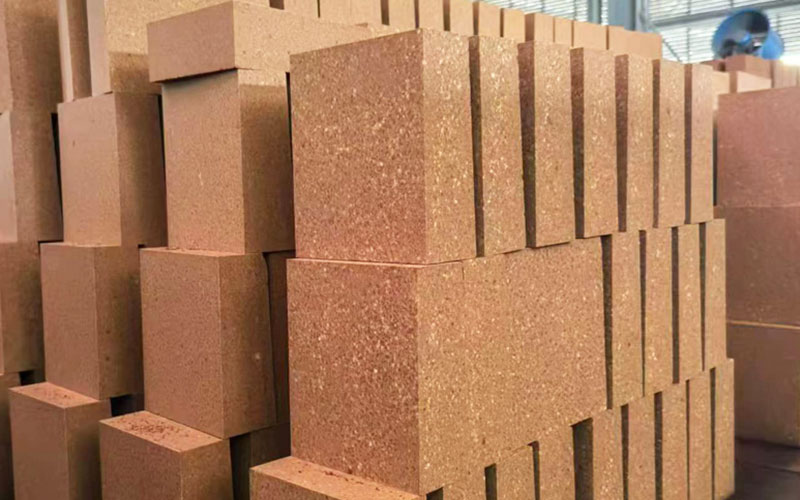
In the modern cement industry, the rotary kiln remains the core equipment that determines clinker quality, production efficiency, and operating cost. As kiln operating temperatures continue to rise and fuel types become more diversified, the demand for high-performance refractory materials has never been greater. Among various refractory solutions, Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns have become one of the most reliable and widely adopted lining materials, especially in high-wear and high-temperature zones.
Choosing the right refractory brick is not only a matter of thermal resistance, but also involves chemical stability, mechanical strength, thermal shock resistance, and long-term cost efficiency. This article explains why Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns are increasingly favored, where they are best applied, and how to select the most suitable grade for different kiln conditions.

Operating Challenges Inside Cement Rotary Kilns
Cement rotary kilns operate under extremely harsh conditions. The internal environment exposes refractory linings to multiple forms of stress simultaneously:
High temperatures, often reaching 1450–1500°C in the burning zone
Chemical corrosion from clinker phases, alkalis, sulfates, and liquid melts
Mechanical abrasion caused by clinker movement and kiln rotation
Thermal shock from frequent startups, shutdowns, and flame fluctuations
Traditional refractory materials such as high-alumina bricks or magnesia bricks alone may struggle to meet all these demands. This is where Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns offer a balanced and superior solution.
What Makes Magnesia Spinel Bricks Suitable for Cement Rotary Kilns
Magnesia spinel bricks are composite refractories made primarily from high-purity magnesia (MgO) and magnesium aluminate spinel (MgAl₂O₄). The combination of these two components creates a brick structure that performs exceptionally well under cement kiln conditions.
Key advantages include:
Excellent resistance to clinker and liquid phase corrosion
Improved thermal shock resistance compared with traditional magnesia bricks
High refractoriness under load
Reduced tendency for structural spalling
Because of these properties, Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns are especially suitable for zones where both temperature and chemical attack are severe.
Chemical Stability Against Cement Kiln Corrosion
One of the most critical requirements for refractories in cement rotary kilns is resistance to chemical corrosion. The kiln atmosphere contains:
Calcium oxide (CaO)
Iron oxide (Fe₂O₃)
Alkalis (Na₂O, K₂O)
Sulfur compounds
Magnesia spinel bricks exhibit excellent chemical compatibility with basic clinker phases. The spinel phase helps prevent deep penetration of liquid phases, while the magnesia matrix maintains structural stability.
Compared with ordinary magnesia bricks, Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns show slower corrosion rates and longer service life, particularly in kilns burning alternative fuels or operating with high alkali loads.

Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Frequent temperature fluctuations are unavoidable in modern cement plants due to:
Production interruptions
Fuel switching
Kiln speed adjustments
Pure magnesia bricks tend to have lower thermal shock resistance, making them prone to cracking and spalling. The introduction of spinel into the brick structure improves elasticity and crack resistance.
This enhancement allows Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns to withstand repeated thermal cycling, reducing unplanned shutdowns and maintenance frequency.
Key Application Zones in Cement Rotary Kilns
Magnesia spinel bricks are not necessarily used throughout the entire kiln but are strategically applied in the most demanding zones.
Burning Zone
The burning zone experiences the highest temperatures and most aggressive chemical attack. Here, Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns offer:
High refractoriness under load
Excellent resistance to clinker melt infiltration
Long service life under stable operation
Transition Zone
In the transition zone, temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress are more pronounced. Magnesia spinel bricks perform well due to their balanced thermal shock resistance and abrasion resistance.
Safety or Lower Burning Zone (Selected Conditions)
In some kiln designs, magnesia spinel bricks are also used in adjacent zones to improve lining continuity and reduce interface stress between different refractory types.
Comparison with Other Refractory Options
When choosing refractory materials for cement rotary kilns, plant engineers often compare several options:
High-Alumina Bricks
Good abrasion resistance
Limited resistance to basic clinker corrosion
Shorter lifespan in high-alkali kilns
Magnesia Chrome Bricks
Excellent performance but environmental concerns related to hexavalent chromium
Increasingly restricted in many regions
Magnesia Spinel Bricks
Chrome-free and environmentally friendly
Balanced resistance to heat, corrosion, and thermal shock
Widely accepted as a sustainable alternative
From both technical and regulatory perspectives, Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns represent a future-proof solution.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Magnesia Spinel Bricks
Not all magnesia spinel bricks are the same. Proper selection depends on several kiln-specific factors:
Spinel Content
Higher spinel content generally improves thermal shock resistance but may affect corrosion resistance. The optimal balance depends on kiln operation stability.
Magnesia Purity
High-purity MgO improves refractoriness and resistance to clinker attack, especially in high-temperature zones.
Apparent Porosity
Lower porosity reduces clinker penetration and corrosion but may increase thermal stress. Controlled porosity design is essential.
Manufacturing Method
Bricks produced with advanced sintering technology show better microstructure, higher strength, and more consistent performance.
Selecting the right grade of Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns should always be based on actual operating data rather than price alone.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Even the best refractory material can fail prematurely if installation and maintenance are improper.
Key recommendations include:
Ensure proper brick orientation and tight joints
Use compatible refractory mortars
Follow controlled heating and cooling schedules
Monitor kiln shell temperature regularly
When installed correctly, Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns can deliver extended campaign life and stable kiln operation.
Cost Performance and Long-Term Value
Although magnesia spinel bricks may have a higher initial cost compared to basic refractories, their long-term value is significant:
Longer service life
Reduced kiln shutdowns
Lower maintenance and labor costs
Improved clinker quality stability
From a total cost of ownership perspective, choosing Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns often results in substantial operational savings.
Conclusion
Selecting the right refractory lining is a strategic decision that directly affects cement kiln performance, safety, and profitability. With their excellent resistance to high temperature, chemical corrosion, and thermal shock, Magnesia Spinel Bricks for cement rotary kilns have proven to be a reliable and cost-effective solution for critical kiln zones.
By understanding kiln operating conditions and choosing the appropriate brick grade, cement producers can significantly extend refractory life, reduce downtime, and improve overall production efficiency. For cement plants aiming for long-term stability and sustainability, magnesia spinel bricks remain a smart and proven choice.
Need help with refractory lining materials or kiln insulation solutions for cement rotary kiln? Contact us for expert consultation and supply of high-performance rotary kiln refractory bricks.