Glass melting furnaces operate under some of the most extreme industrial conditions, combining ultra-high temperatures, aggressive chemical atmospheres, molten glass corrosion, and continuous long-term operation. In this environment, the selection and application of refractory materials for glass melting furnaces directly determine furnace efficiency, glass quality, energy consumption, and overall service life.
Rather than serving a single function, refractory materials play multiple critical roles across different furnace zones. Each application area within a glass melting furnace places unique thermal, chemical, and mechanical demands on refractory linings. Understanding how refractory materials are applied in these zones is essential for optimizing furnace performance and minimizing unplanned shutdowns.
This article focuses on the practical application of refractory materials for glass melting furnaces, analyzing how different refractory solutions are used in key furnace sections and why proper material selection is vital for modern glass production.
Working Environment of Glass Melting Furnaces
Before examining specific applications, it is important to recognize the operational challenges that define glass melting furnaces. These furnaces typically operate at temperatures ranging from 1400°C to over 1600°C and are often required to run continuously for several years without interruption.
During operation, refractory materials are exposed to:
Constant contact with molten glass and aggressive batch materials
Chemical attack from alkali vapors, boron compounds, and other fluxes
Thermal cycling during startup, shutdown, and load fluctuations
Mechanical erosion caused by glass flow and batch movement
These harsh conditions explain why refractory materials for glass melting furnaces must be carefully matched to their application zone rather than chosen as a one-size-fits-all solution.
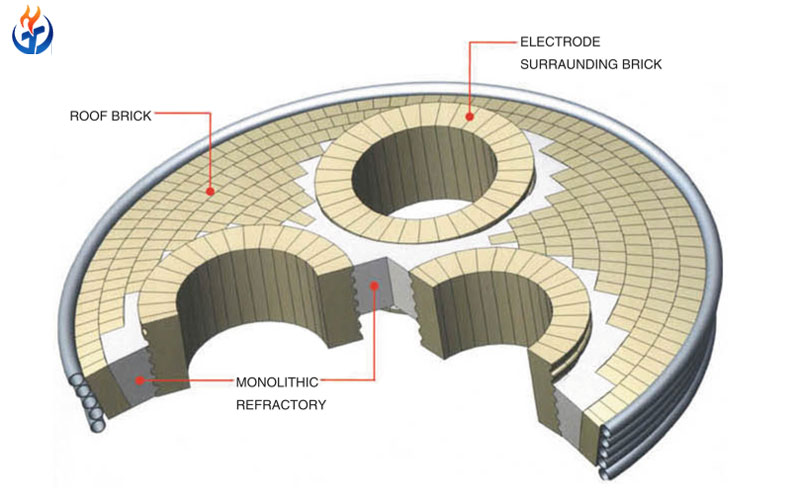
Application in Furnace Superstructure Areas
The furnace superstructure, including the crown and sidewalls above the glass melt, is one of the most demanding application zones. This area is continuously exposed to high temperatures and aggressive vapors released from molten glass and raw materials.
Crown Refractory Applications
The crown is typically constructed using silica-based refractory materials. In this application, silica refractories offer excellent performance due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist deformation under load.
Key performance requirements for crown refractories include:
High refractoriness and low creep at elevated temperatures
Resistance to alkali vapor corrosion
Dimensional stability over long campaigns
Silica refractories remain a common choice because they form a protective viscous layer when exposed to alkali vapors, extending service life in crown applications.
Upper Sidewall Applications
Upper sidewalls also fall under the superstructure category but experience additional thermal gradients. Here, refractory materials for glass melting furnaces must balance insulation performance with chemical resistance.
High-purity alumina or mullite-based refractories are often applied in these zones, providing improved resistance to alkali attack while maintaining sufficient mechanical strength.
Application in Glass Contact Areas
Glass contact zones represent the most critical application of refractory materials for glass melting furnaces. Any degradation or contamination in these areas can directly affect glass quality.
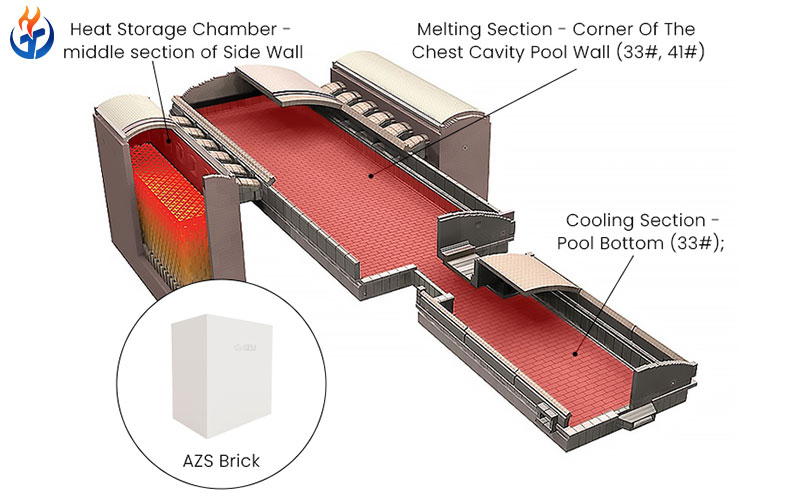
Tank Bottom and Sidewall Applications
The tank bottom and lower sidewalls are continuously in contact with molten glass, making corrosion resistance the primary requirement. In these applications, fused cast refractories are widely used.
Fused cast AZS (alumina-zirconia-silica) materials are especially valued for:
Exceptional resistance to glass corrosion
Minimal glass contamination
Long service life in high-temperature environments
The zirconia content in AZS refractories significantly enhances resistance to aggressive glass compositions, making them a standard choice for container glass, float glass, and specialty glass furnaces.
Throat and Dam Applications
The throat area controls glass flow from the melting zone to the refining zone. Refractory materials in this application must withstand both chemical corrosion and severe mechanical erosion.
High-zirconia refractories are commonly applied here due to their:
Superior erosion resistance
Stability under turbulent glass flow
Reduced risk of blister or stone formation
The precise application of refractory materials in throat areas plays a key role in ensuring consistent glass flow and stable furnace operation.
Application in Melting and Refining Zones
The melting and refining zones impose different requirements on refractory materials for glass melting furnaces.
Melting Zone Applications
In the melting zone, refractories must resist attack from raw batch materials that are not yet fully melted. These materials often contain alkalis, sulfates, and other reactive components.
Dense alumina and mullite refractories are commonly applied here because they provide:
Strong resistance to chemical attack from batch materials
Adequate thermal shock resistance
Structural stability under fluctuating thermal loads
Proper application in the melting zone helps reduce refractory wear and limits the introduction of defects into the molten glass.
Refining Zone Applications
The refining zone allows gases and bubbles to escape from molten glass. Refractory materials used here must offer excellent corrosion resistance while minimizing interaction with the glass.
High-purity alumina and AZS refractories are often selected for refining zone applications due to their low contamination potential and long-term stability.
Application in Forehearth and Conditioning Areas
After refining, molten glass flows through the forehearth system, where temperature control becomes critical. Refractory materials for glass melting furnaces used in these areas must support precise thermal regulation.
Forehearth Channel Applications
Forehearth channels require refractories with:
Good thermal insulation properties
Resistance to glass corrosion at lower temperatures
Smooth surfaces to promote stable glass flow
Sillimanite, mullite, and alumina-based refractories are commonly applied in forehearth channels, providing a balance between insulation efficiency and durability.
Spout and Delivery Applications
Spouts and delivery systems experience localized wear due to constant glass flow. High-density, low-porosity refractories are preferred in these applications to reduce erosion and extend service life.
Application in Furnace Insulation Systems
Beyond hot-face refractories, insulation layers play a vital role in overall furnace efficiency. The correct application of insulating refractory materials for glass melting furnaces can significantly reduce heat loss and energy consumption.
Backup Lining Applications
Lightweight insulating bricks and refractory fibers are commonly applied as backup linings behind dense working layers. These materials offer:
Low thermal conductivity
Reduced shell temperature
Improved energy efficiency
Proper layering of working refractories and insulation materials ensures both structural integrity and thermal performance.
Conclusion
The application of refractory materials for glass melting furnaces is a complex, zone-specific process that directly affects furnace performance, glass quality, and operating costs. From crown and superstructure areas to glass contact zones, forehearths, and insulation systems, each application demands carefully selected refractory solutions.
By understanding how refractory materials are applied in different sections of a glass melting furnace, manufacturers and engineers can optimize furnace design, extend service life, and achieve more stable and efficient glass production. Proper material selection, professional installation, and ongoing maintenance together form the foundation of successful refractory application in modern glass melting furnaces.
Looking for refractory solutions for glass melting furnaces? Contact our technical team today for custom recommendations, product samples, and installation support. Welcome to contact Xintai Refractory.