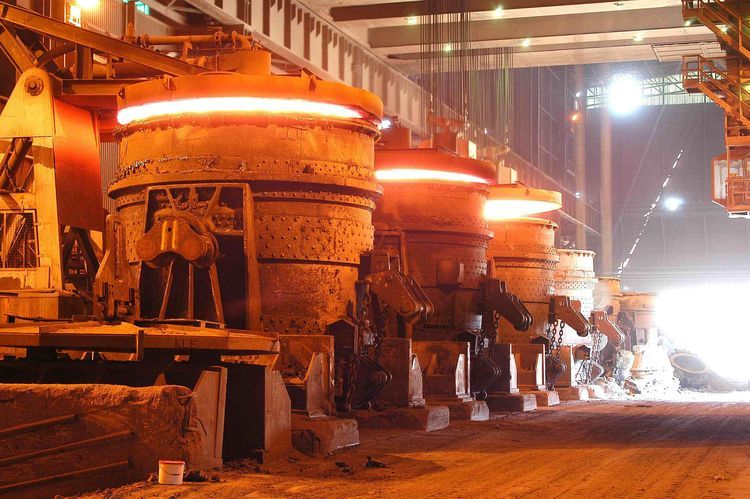
Lightweight silica bricks are a specialized type of refractory material widely used in various high-temperature industrial applications. Their unique combination of low bulk density, excellent thermal insulation, and high-temperature resistance makes them indispensable in many thermal equipment systems. This article will explore in depth the application of lightweight silica bricks, including their characteristics, advantages, performance properties, and key industries where they are most commonly used.

Introduction to Lightweight Silica Bricks
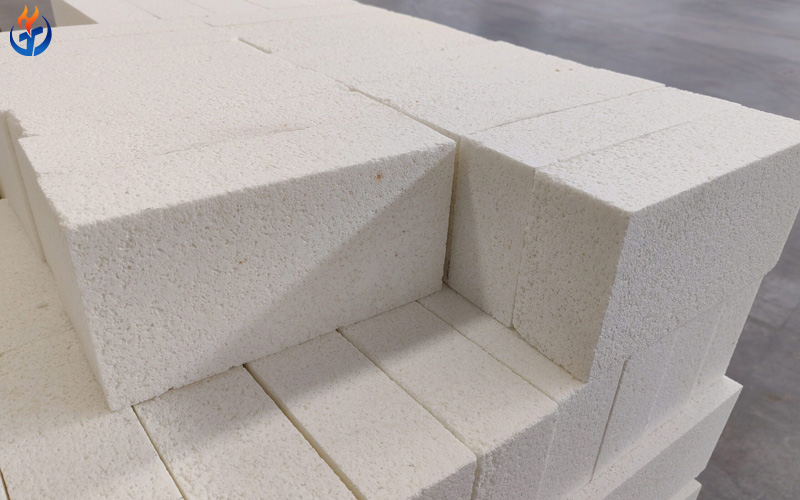
Lightweight silica bricks, also known as lightweight silicon bricks or porous silica bricks, are made primarily from silica (SiO₂) as the main raw material. Their silica content typically exceeds 91%, and their bulk density ranges from 0.8 to 1.2 g/cm³, depending on the grade and manufacturing process.
They are produced using crystalline silica (such as quartz sand, quartzite, or ganister) combined with a foaming or combustible agent. During firing, these additives burn out, leaving behind a porous structure. The result is a lightweight, thermally efficient refractory brick that can withstand high temperatures while minimizing heat loss.
Key Properties of Lightweight Silica Bricks
Before exploring their applications, it’s important to understand what makes lightweight silica bricks so suitable for high-temperature industries. Some of the most important properties include:
(1) High Silica Content
With more than 91% SiO₂, lightweight silica bricks exhibit excellent refractoriness—up to 1650°C–1760°C. This high silica concentration ensures chemical stability in oxidizing atmospheres.
(2) Low Thermal Conductivity
The porous structure of the brick reduces heat transfer, making it an ideal insulating refractory material. This helps maintain furnace temperature while minimizing heat loss, improving energy efficiency.
(3) Excellent Thermal Stability
Silica bricks have strong resistance to thermal shock within certain limits. They can handle gradual heating and cooling cycles without cracking, provided the temperature changes are not extremely rapid.
(4) Lightweight and Easy to Install
Their lower bulk density means reduced load on the furnace structure, making installation faster and less labor-intensive.
(5) High Load Softening Temperature
Lightweight silica bricks maintain good structural strength at elevated temperatures, with a softening point under load around 1500°C.
Manufacturing Process of Lightweight Silica Bricks
Understanding the manufacturing process provides insights into why these bricks perform so well in specific applications. The general process includes:
Raw Material Selection:
High-purity silica (usually quartzite or vein quartz) is crushed and finely ground.Mixing and Foaming:
Foaming agents or combustible materials such as sawdust, paper pulp, or organic resin are added to create pores after burning.Molding:
The mixture is shaped under moderate pressure into bricks of standard or customized sizes.Drying:
The molded bricks are dried at low temperatures to remove moisture.Firing:
Finally, the bricks are fired in kilns at temperatures of around 1350–1450°C, during which the silica undergoes transformation to tridymite and cristobalite phases, giving the brick its refractoriness.
Applications of Lightweight Silica Bricks in Various Industries
Now, let’s discuss the main application areas of lightweight silica bricks across industries that operate at high temperatures.
4.1. Glass Industry
The glass industry is one of the largest consumers of lightweight silica bricks. These bricks are used mainly for thermal insulation in the upper structures of glass melting furnaces, including:
Crown (arch roof) insulation
Regenerator checkers
Sidewalls and flues
Silica bricks perform well in glass furnaces because they resist the corrosive action of alkali vapors and maintain strength at high operating temperatures around 1600°C. Their low thermal conductivity helps reduce heat loss through the furnace roof, improving fuel efficiency and glass quality.
4.2. Coke Oven and By-Product Plants
In the coke-making industry, lightweight silica bricks are used as insulation lining materials for coke ovens. They are typically installed behind dense silica bricks or refractory clay bricks to retain heat within the oven chamber.
Applications include:
Coke oven roofs and sidewalls
Combustion chambers
Hot-air flues
Their dimensional stability and resistance to high-temperature creep make them ideal for these long-cycle operations.
4.3. Iron and Steel Industry
In the iron and steel industry, high temperatures are common in furnaces such as hot blast stoves, open-hearth furnaces, and ladles. Lightweight silica bricks serve primarily as insulation materials in the upper parts of these furnaces, helping maintain thermal balance while reducing heat loss.
Specific applications:
Hot blast stove domes and upper walls
Insulating layers in steel ladles and tundishes
Soaking pit walls
Their resistance to acidic slags also makes them a better choice than alumina-based bricks in oxidizing conditions.
4.4. Ceramic Industry
The ceramic industry uses lightweight silica bricks in tunnel kilns and shuttle kilns where high temperature stability and insulation are crucial.
Key benefits in ceramic kilns:
Reduced energy consumption due to better insulation.
Uniform heat distribution for consistent firing quality.
Lightweight construction that reduces structural load.
Lightweight silica bricks are often used as the insulating layer in the kiln wall and roof, paired with denser refractory bricks that face direct flame contact.
4.5. Non-Ferrous Metal Industry
In the non-ferrous metal sector (such as aluminum, copper, and zinc refining), maintaining stable temperatures during smelting and refining is essential. Lightweight silica bricks are used as backup insulation layers in furnaces and reactors to minimize heat loss.
Their inert chemical nature ensures that they do not react with molten metals or fluxes, thus maintaining purity and improving furnace service life.
4.6. Chemical Industry
Many chemical processes—such as the production of fertilizers, acids, or petrochemicals—require high-temperature reactors or regenerators. Lightweight silica bricks are used in:
Catalyst support furnaces
Reforming reactors
Sulfuric acid converters
They provide both insulation and corrosion resistance, ensuring stable operation and improved energy utilization.
4.7. Power Generation
In thermal power plants, especially those with coal gasification or waste heat boilers, lightweight silica bricks are used in high-temperature zones such as boiler linings, regenerators, and heat exchangers.
Their ability to withstand high radiant heat without deformation enhances the overall safety and durability of the system.
Advantages of Using Lightweight Silica Bricks
Lightweight silica bricks are not just preferred for their insulating ability. They offer several operational and economic advantages that make them highly cost-effective:
Energy Savings:
By reducing heat loss, they significantly lower fuel consumption.Extended Equipment Life:
Their thermal stability reduces stress on the main refractory lining, extending service life.Lower Installation Costs:
The lightweight nature reduces handling and structural requirements.Environmentally Friendly:
Improved fuel efficiency leads to lower CO₂ emissions.Consistent Furnace Performance:
Stable insulation results in uniform temperatures, improving product quality.
Comparison with Other Insulating Bricks
| Property | Lightweight Silica Brick | Lightweight Mullite Brick | Insulating Fire Brick |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Component | SiO₂ (>91%) | Al₂O₃ (60–70%) | Al₂O₃ + SiO₂ |
| Max Service Temp | 1550–1650°C | 1600–1700°C | 1250–1400°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Resistance to Alkali | Excellent | Fair | Fair |
| Typical Use | Coke ovens, glass furnaces | Kilns, heaters | Low-temp furnaces |
This comparison shows that lightweight silica bricks outperform other insulating materials when operating temperatures exceed 1500°C, particularly in acidic or oxidizing atmospheres.
Conclusion
The application of lightweight silica bricks spans across multiple high-temperature industries—from glass and steel production to ceramics, chemicals, and energy generation. Their exceptional thermal insulation, chemical stability, and high-temperature endurance make them one of the most efficient and durable refractory insulation materials available today.
By reducing energy consumption and enhancing furnace performance, lightweight silica bricks not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to sustainable industrial development. Whether used as the main insulation lining or as a backup layer, these bricks play an essential role in modern thermal engineering.
Contact Xintai Refractory today for expert support and high-quality lightweight silica bricks — engineered to optimize glass furnace crowns with superior insulation performance, enhanced energy efficiency, and long-lasting durability.