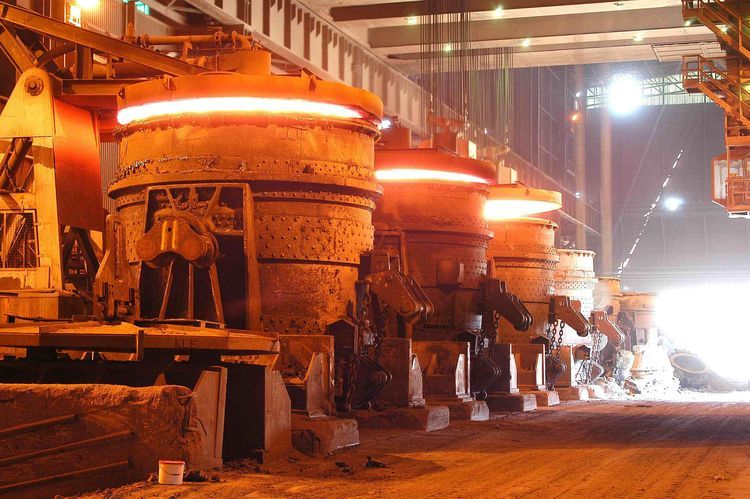
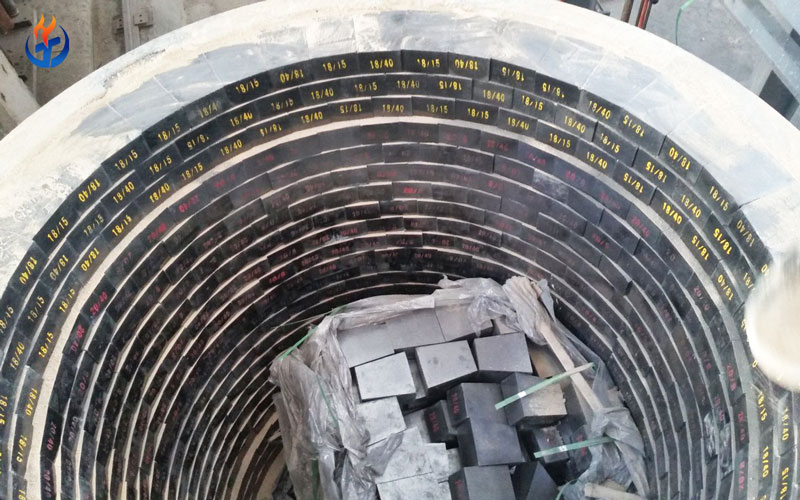
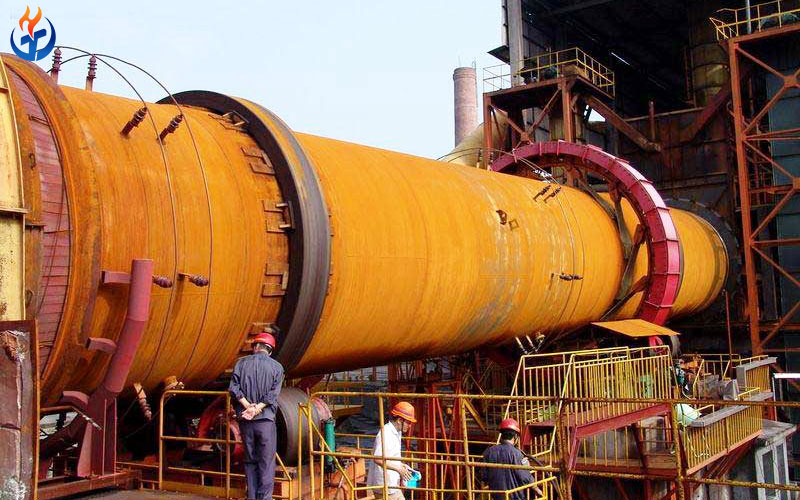
In the demanding environment of cement production, where temperatures soar beyond 1450°C and chemical reactions are continuous and intense, the importance of refractory bricks cannot be overstated. These bricks form the thermal backbone of kilns, preheaters, calciners, coolers, and other high-temperature areas in a cement plant. Their primary purpose is to protect industrial equipment from thermal wear, mechanical abrasion, and chemical corrosion, all while ensuring process efficiency and extended equipment lifespan.
This article explores the application of refractory bricks in the cement industry, covering key installation areas, material types, selection considerations, and how proper brick usage contributes to plant productivity and safety.

Why Refractory Bricks Are Essential in Cement Manufacturing
Cement production is a thermally intensive process, relying on rotary kilns and associated systems to calcine raw materials into clinker. The internal surfaces of this equipment face:
Extreme temperatures (up to 1450°C in kilns)
Highly abrasive dust flows
Corrosive gas and chemical attack
Frequent thermal cycling
Refractory bricks for cement industry are engineered to resist these stressors. Without them, critical components like rotary kilns, kiln hoods, and coolers would quickly deteriorate, leading to unplanned shutdowns, safety hazards, and production losses.
Key Areas Where Refractory Bricks Are Used in Cement Plants
1. Rotary Kilns
The rotary kiln is the heart of cement production. It’s a long cylindrical steel shell lined with refractory bricks that rotate and incline slightly to facilitate raw meal movement and calcination.
Lining Requirements:
Withstand sustained temperatures above 1350°C
Resist abrasion from moving clinker
Withstand chemical attack from alkalis and sulphates
Common Refractory Bricks Used:
Magnesia-spinel bricks (excellent thermal shock resistance)
Magnesia-chrome bricks (for high load-bearing capacity)
High-alumina bricks (in less aggressive zones)
2. Preheaters and Calciners
In dry-process cement plants, preheaters and calciners rapidly preheat raw meal and facilitate partial decarbonation before entering the kiln.
Challenges:
High-speed dust-laden gas flow
Abrasive wear
Alkali and sulfur attack
Refractory Brick Requirements:
Abrasion resistance
Good thermal insulation
Resistance to alkali vapor penetration
Typical Choices:
Alumina-silica bricks
Dense insulating bricks
3. Kiln Hood and Tertiary Air Ducts
The kiln hood connects the kiln to the cooler, while the tertiary air duct recycles hot air back to the calciner.
Hazards Faced:
Thermal shock from clinker discharge
Gas turbulence
Mechanical damage during maintenance
Brick Requirements:
Thermal cycling resistance
Easy installation and replacement
High mechanical strength
Common Refractory Options:
Magnesia-alumina spinel bricks
Precast refractory blocks (for quick maintenance)
4. Coolers and Clinker Discharge Zones
Clinker coolers rapidly cool down hot clinker from the kiln to manageable temperatures while recovering heat.
Challenges:
High abrasion from falling clinker
Thermal cycling due to cooling air
Erosion at grates and slopes
Refractory Solutions:
Chrome-corundum bricks
Zircon-mullite bricks (for extreme wear zones)
5. Other Areas
Burner pipes: Require shape-customized refractory bricks with excellent heat resistance and low thermal conductivity.
Smoke chambers: Face acidic gas attack, use acid-resistant bricks.
Chimneys and stacks: Lined with lightweight refractory bricks for insulation.
Characteristics of Refractory Bricks Used in Cement Industry
When selecting refractory bricks for cement industry applications, key properties to evaluate include:
| Property | Relevance |
|---|---|
| Refractoriness (>1700°C) | Withstand kiln temperatures |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Minimize cracking during cycling |
| Mechanical Strength | Resist abrasion and impact |
| Chemical Resistance | Withstand alkali, sulfur, and clinker attack |
| Bulk Density & Porosity | Influence heat transfer and corrosion resistance |
| Thermal Conductivity | Impacts energy efficiency |
Types of Refractory Bricks Commonly Used
| Refractory Type | Applications |
|---|---|
| Magnesia Bricks | Burning zone of rotary kilns |
| Magnesia-Spinel Bricks | Transition zones (hot end) |
| High-Alumina Bricks | Calciners, kiln inlets |
| Chrome-Magnesia Bricks | Clinker coolers, kiln hood |
| Zircon-Mullite Bricks | Extreme wear zones (discharge ends) |
| Insulating Firebricks | Back-up layers and preheaters |
What Happens When You Use the Wrong Refractory Brick?
Improper refractory selection leads to:
Premature spalling and cracks
Increased heat loss
Frequent relining and high maintenance costs
Production downtime and reduced output
Kiln shell deformation
Thus, optimizing cement rotary kiln lining is not just about insulation, but also productivity and cost control.
Xintai Refractory: Your Cement Plant Partner
Xintai Refractory has been supplying high-performance refractory bricks for cement kilns and related equipment for over 20 years. Our materials are precisely engineered for each section of the production line, ensuring:
✔️ Longer lining life
✔️ Stable kiln operation
✔️ Lower energy consumption
✔️ Reduced maintenance time
Our Products Include:
Magnesia bricks and spinel bricks for kilns
Alumina-silica bricks for preheaters and calciners
Chrome-alumina bricks for coolers
Custom precast blocks for burner pipes and kiln hoods
Insulating bricks for energy-saving back linings
Whether you operate a gray cement plant or a specialized white cement facility, we tailor refractory solutions to your process conditions and budget.
Conclusion
The application of refractory bricks in cement industry is fundamental to both operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. From the high-heat environment of rotary kilns to the abrasive zones of clinker coolers, each area demands a specific refractory design.
Choosing the right cement industry refractory can:
Extend equipment lifespan
Reduce energy costs
Improve safety and sustainability
Maximize overall productivity
Looking for a reliable supplier of refractory bricks for cement kilns?
Xintai Refractory offers expert-engineered refractory products for every part of your cement production line.
📩 Contact us today to receive customized solutions and a free technical consultation.
With two decades of experience serving cement plants globally, we’re ready to support your thermal performance goals.