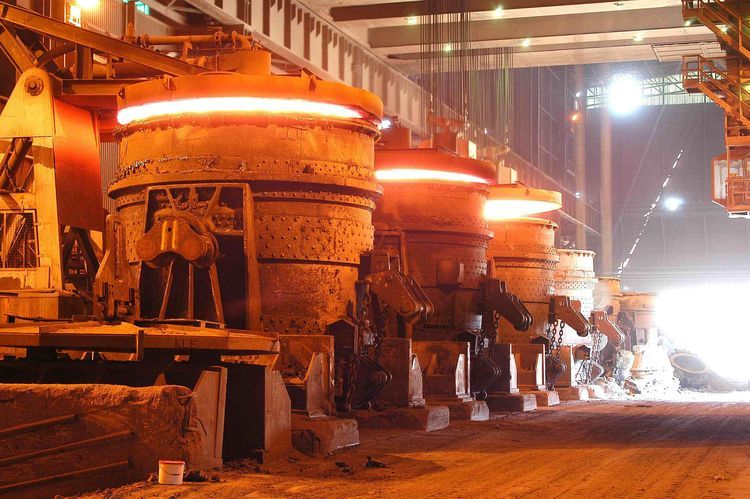
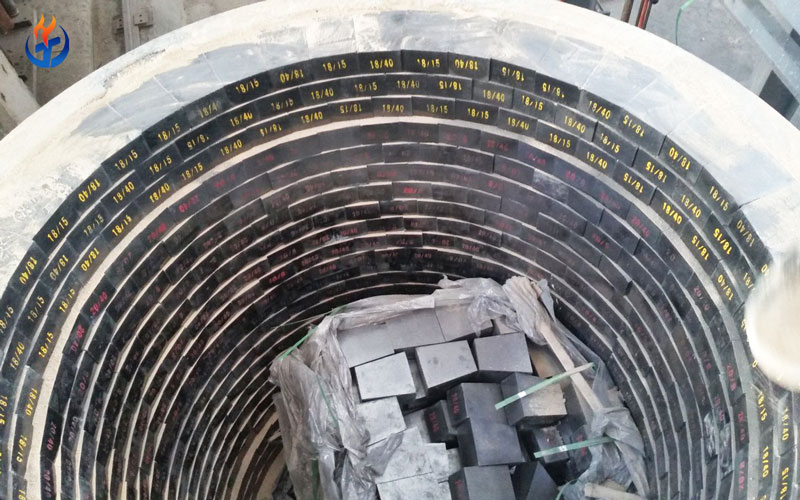
In modern steelmaking, ladle refining has become a crucial step to improve steel quality, reduce impurities, and stabilize composition. Whether the plant uses a Vacuum Arc Degassing (VAD) furnace, an ASEA-SKF refining furnace, or other secondary metallurgy units, the Refractory Lining for Ladle determines operational stability, refining temperature control, and the overall lifecycle cost.
Xintai Refractory, a professional refractory manufacturer with over 20 years of experience, provides a complete solution for ladle lining selection. This guide will help steelmakers understand how to choose the best refractory materials for ladle refining equipment.

Introduction to Ladle Refining Equipment
Ladle refining equipment mainly includes technologies such as:
VAD Furnace (Vacuum Arc Degassing)
Molten steel is injected into the ladle and placed inside a vacuum chamber where it undergoes:
Vacuum degassing
Electric arc heating
This operation requires the refractory lining to withstand high temperature, high vacuum, strong thermal shocks, and erosion by slag and steel.
ASEA-SKF Furnace
ASEA-SKF refining involves:
Electric arc heating
Vacuum treatment
Electromagnetic stirring, which causes additional wear and turbulence
These rapid temperature changes and forceful flows expose the ladle lining to far more severe working conditions than ordinary steelmaking furnaces.
The progress of ladle refining technology has significantly increased the demands placed on Refractory Lining for Ladle. Choosing the wrong refractory can lead to:
Short lining life
Frequent relining shutdowns
High production cost
Steel contamination
Therefore, steel plants must follow scientific principles when selecting refractory materials.
Key Factors Affecting Refractory Lining Wear in Ladle Refining
Even with insulation boards and advanced ladle covers, the thermal cycling in ladle refining remains intense. The main causes of refractory lining damage include:
2.1 Strong Thermal Cycling
During tapping, transporting, refining, and emptying, the ladle repeatedly undergoes:
Rapid heating
Rapid cooling
This causes deep thermomechanical cracks in the working lining.
2.2 High Steel Temperature
Refining requires higher tapping temperatures. Steel above 1650–1750°C accelerates:
Melting erosion
Oxidation
Slag penetration in refractory bricks
2.3 Aggressive Slag Composition
Refining slag often contains:
Lime (CaO)
Calcium aluminate
Fluorite (CaF₂)
These compounds create high-penetration, highly erosive slags with fast dissolution rates.
2.4 Stirring-Induced Erosion
Forced stirring—mechanical, argon bubbling, or electromagnetic—causes molten steel to scour the lining at high velocity, wearing down the refractory surface.
2.5 Lack of Protection Layers
Unlike primary steelmaking furnaces:
Ladles often lack sufficient slag coating
Spray repair is not performed frequently
This exposes the refractory lining directly to molten steel.
2.6 Vacuum-Induced Volatilization
Under vacuum:
C, Si, Al, Ti, Mn in molten steel may react with refractory components
Some refractory minerals volatilize or lose mass
This leads to structural weakening and early failure.
Understanding these factors helps steel plants select the most durable and economical materials.
Key Requirements for Refractory Lining for Ladle Refining Equipment
To guarantee long service life and safe operation, the refractory lining must meet the following performance criteria:
3.1 High Corrosion Resistance
At refining temperatures above 1750°C, refractory materials must resist:
Chemical attack from basic and acidic slags
Dissolution from molten steel
Structural degradation
Corundum (Al₂O₃) bricks and alumina-magnesia refractories are common solutions because they perform well under variable slag alkalinity (0.6%–4.0%). They prevent:
Slag line wear
Steel infiltration
Unwanted reactions with alloy elements
3.2 High Penetration Resistance
Refining slags are highly fluid and aggressive. Without adequate penetration resistance, slags:
Enter pores of the refractory
Cause micro-cracking
Lead to spalling and structural peeling
Materials with:
Low porosity
Dense microstructure
Optimized bonding phases
are ideal for maintaining long service life.
3.3 High Wear Resistance
During electromagnetic or argon stirring, molten steel can reach extremely high turbulence speeds. A suitable refractory lining must therefore have:
High mechanical strength
Abrasion resistance
Resistance to erosion by steel flow and slag flow
Alumina-magnesia carbon bricks, burned magnesia-chrome bricks, and spinel-reinforced castables are commonly selected for these zones.
3.4 Excellent Vacuum Stability
Refractory materials must remain stable under vacuum. Tests show:
Al₂O₃, ZrO₂, and CaO-based refractories exhibit excellent stability
MgO, SiO₂, Cr₂O₃ may lose weight or volatilize at high temperatures
Although low temperatures have minimal effect, refining ladles often reach temperature + vacuum conditions where volatilization becomes significant. Choosing vacuum-stable refractories reduces mass loss and ensures lining integrity.
3.5 High Thermal Shock Resistance
Ladle operation involves:
Intermittent heating
High-frequency temperature cycling
Rapid quenching and reheating
Refractory materials must absorb thermal stress without cracking or spalling.
Recommended materials include:
High-purity alumina castables
Alumina-spinel bricks
High-strength, low-porosity monolithics
Their flexibility and stable microstructure ensure they survive repeated thermal shocks.
Recommended Xintai Refractory Products for Ladle Lining
Based on the above performance requirements, Xintai Refractory offers a full range of materials tailor-made for ladle refining:
Working Lining Materials
High-purity alumina bricks
Alumina-magnesia spinel bricks
Magnesia-carbon and alumina-carbon bricks
Corundum-based refractories
Safety Lining Materials
High-alumina bricks
Lightweight castables
Insulating bricks
Monolithic Refractories
Alumina-spinel castables
Low-cement high-alumina castables
Slag-resistant gunning mixes
Each product is designed to withstand complex refining conditions and ensure stable ladle performance.
How to Select the Right Refractory Lining for Your Ladle
When choosing a Refractory Lining for Ladle, consider the following:
- Type of refining furnace (VAD, LF, ASEA-SKF)
- Operating temperature and steel grade
- Slag composition and its fluidity
- Stirring method and intensity
- Vacuum level and operation frequency
- Expected service life and maintenance strategy
- Cost-performance ratio
Xintai Refractory provides customized solutions based on real operating conditions to help steel plants achieve:
Longer ladle life
Stable refining temperature
Lower refractory consumption
Reduced breakdown time
Conclusion
Choosing the right Refractory Lining for Ladle is critical to the performance and service life of ladle refining equipment. VAD and ASEA-SKF furnaces subject refractory linings to extreme thermal, chemical, and mechanical stresses. Therefore, steelmakers must choose materials with strong corrosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, wear resistance, penetration resistance, and vacuum stability.
Xintai Refractory offers complete ladle lining solutions backed by advanced production technology and professional support. If you need high-quality refractory materials for steel ladles or want expert advice on your current ladle lining design, feel free to contact us anytime.
Xintai Refractory – Professional, Reliable, and Dedicated to Your Steelmaking Success.