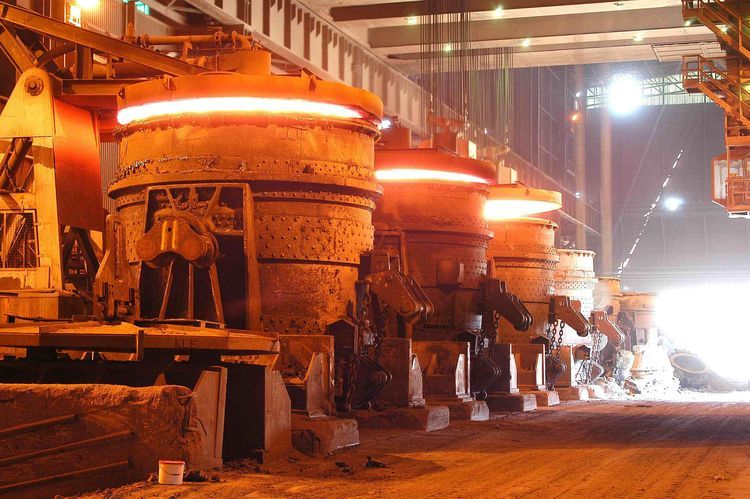
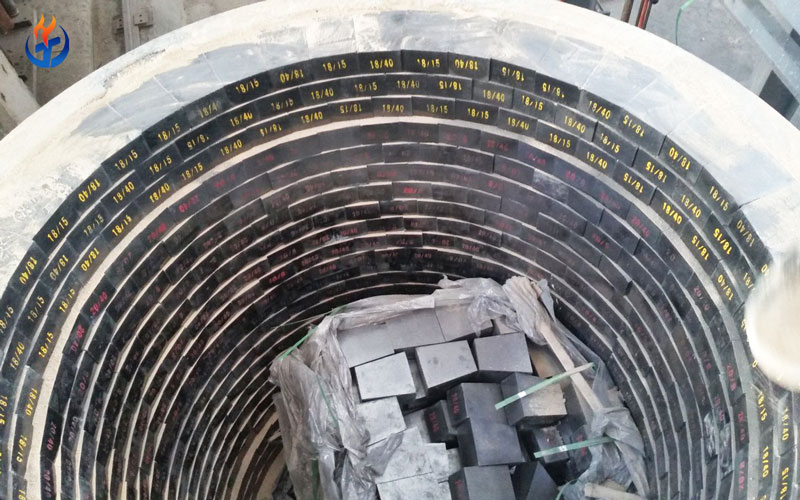
Silica bricks are among the most important refractory materials used in the construction of glass furnaces, particularly in the furnace crown, due to their excellent resistance to high temperatures and the ability to withstand long-term thermal load. The glass industry places extremely high demands on refractory materials, especially in the melting area and the crown section, where temperatures can exceed 1600°C. In this article, we’ll explore the use of silica bricks in glass furnace crowns, their characteristics, advantages, and maintenance considerations — and why they are indispensable in the production of high-quality glass.
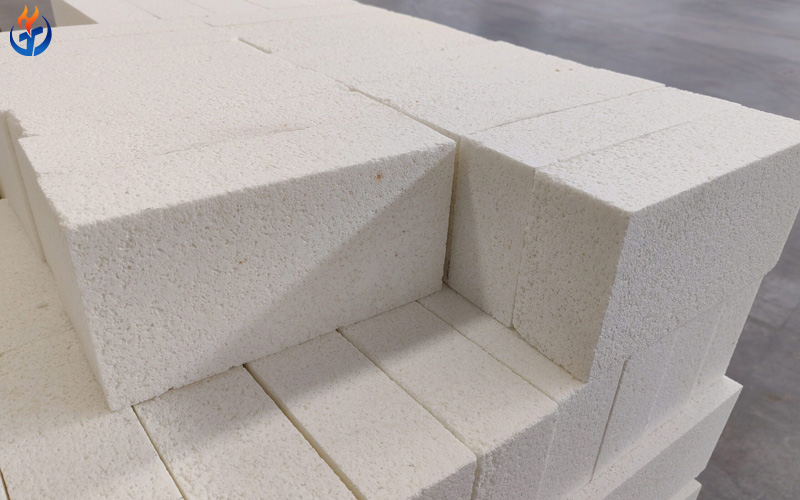

Introduction to Silica Bricks
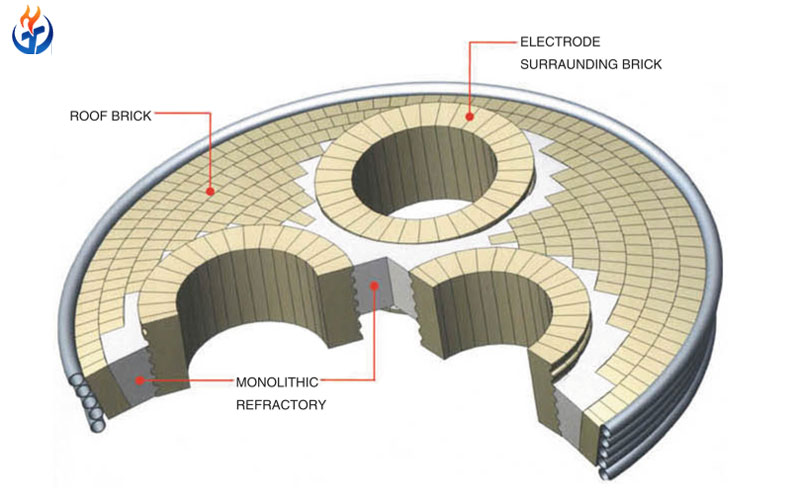
The glass furnace crown is the uppermost part of a glass melting furnace. It directly faces the combustion flame and hot gases, meaning it experiences the highest thermal stress and corrosion from volatile components. Therefore, the crown material must have high refractoriness, low deformation, strong chemical stability, and excellent resistance to creep.
Silica bricks meet these requirements perfectly due to several reasons:
High Refractoriness Under Load:
Silica bricks maintain strength and shape at temperatures exceeding 1650°C, which is critical for glass furnace crowns operating continuously under extreme conditions.Low Thermal Expansion and Good Volume Stability:
Once the silica brick is heated beyond 600°C, it undergoes a permanent volume change that stabilizes during service, reducing the risk of cracking or spalling.Excellent Creep Resistance:
The crown structure must remain stable for years. Silica bricks’ high creep resistance ensures that the arch-shaped structure doesn’t deform or collapse even after long-term high-temperature exposure.Resistance to Acidic Vapors:
Silica bricks resist attack from acidic gases such as SO₂ and volatile glass components, which are common in glass melting operations.Thermal Conductivity and Insulation:
While silica bricks are not as insulating as lightweight materials, their moderate thermal conductivity helps maintain a balanced temperature gradient across the furnace crown, avoiding sharp temperature fluctuations that can cause thermal shock.
Silica bricks are a type of acid refractory made mainly from quartzite or flint with the addition of a small amount of mineralizer such as lime. The main component of silica brick is SiO₂, with a purity of over 94%. After being shaped and fired at high temperature, silica bricks develop a strong structure of tridymite and cristobalite crystals, giving them outstanding thermal and mechanical properties.
Because silica bricks can maintain their structural integrity and strength even at very high temperatures, they are often chosen for parts of industrial furnaces that face continuous thermal load — such as the crowns of glass melting furnaces, coke ovens, and hot blast stoves.
Composition and Manufacturing of Silica Bricks for Glass Furnaces
Silica bricks used in glass furnace crowns are typically made from natural quartzite as the main raw material. The production process includes:
Raw Material Selection:
High-purity quartzite with minimal impurities (especially Al₂O₃ and Fe₂O₃) is selected to ensure stable chemical composition and melting behavior.Crushing and Grading:
The quartzite is crushed and screened into various particle sizes for proper packing density and sintering behavior.Adding Binder and Mineralizer:
Lime or other fluxing agents are added in small quantities to promote the transformation of quartz to tridymite and cristobalite during firing.Forming:
The mixture is pressed into bricks under high pressure to achieve the required shape and density.Drying and Firing:
The bricks are slowly dried and then fired at around 1450°C–1550°C in a kiln. During firing, the quartz transforms into tridymite and cristobalite, which are responsible for the high-temperature strength and stability of silica bricks.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Typical properties of silica bricks used in glass furnace crowns include:
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| SiO₂ content | ≥ 94–96% |
| Apparent porosity | ≤ 22% |
| Cold crushing strength | ≥ 35 MPa |
| Refractoriness under load (0.2 MPa) | ≥ 1650°C |
| True density | 2.34 g/cm³ |
| Thermal expansion (1000°C) | ~1.3% |
These properties make silica bricks ideal for high-temperature, high-load applications where chemical stability and structural integrity are crucial.
Structure of a Glass Furnace and the Crown’s Role
A glass melting furnace typically consists of several zones: the melting tank, refiner, working end, and the crown. The crown (or roof) is one of the most critical parts — it encloses the combustion chamber and reflects heat back into the melt.
In most furnaces, the crown is constructed in an arched shape using pre-shaped silica bricks. The arch design distributes weight evenly and withstands thermal stress effectively. The crown’s performance directly influences fuel efficiency, temperature uniformity, and furnace lifespan.
Comparison with Other Crown Refractories
While silica bricks are dominant in most glass furnaces, other materials are also used depending on the glass type:
| Material | Application | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silica Bricks | Soda-lime, container glass | High-temperature strength, stability | Brittle, sensitive to alkali vapor |
| Zircon Bricks | High-quality optical or borosilicate glass | Excellent corrosion resistance | Expensive |
| Alumina Bricks | Specialty glass furnaces | Good strength, moderate cost | Lower refractoriness under load |
| Fused-Cast AZS | Regenerator or throat zones | Excellent wear resistance | Not suitable for crowns |
Among them, silica bricks remain the preferred choice for most furnace crowns due to their balance of performance, stability, and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
The use of silica bricks in glass furnace crowns remains one of the most reliable and cost-effective solutions in the refractory industry. Their high refractoriness under load, excellent volume stability, chemical resistance, and low creep rate make them ideal for long-term, high-temperature service.
For glass manufacturers seeking both performance and durability, silica bricks provide the stability necessary to maintain furnace structure and glass quality over years of continuous operation. Even as new refractory technologies emerge, silica bricks continue to prove their unmatched value in glass furnace crown applications — a testament to their engineering excellence and irreplaceable role in the modern glass industry.
Contact Xintai Refractory today for professional guidance and premium silica refractory bricks, designed to enhance your glass furnace crowns with reliable performance, improved energy efficiency, and extended service life.